Electrodialysis Reversal System – Toxic Metal Removal in Industrial Wastewater
Introduction:
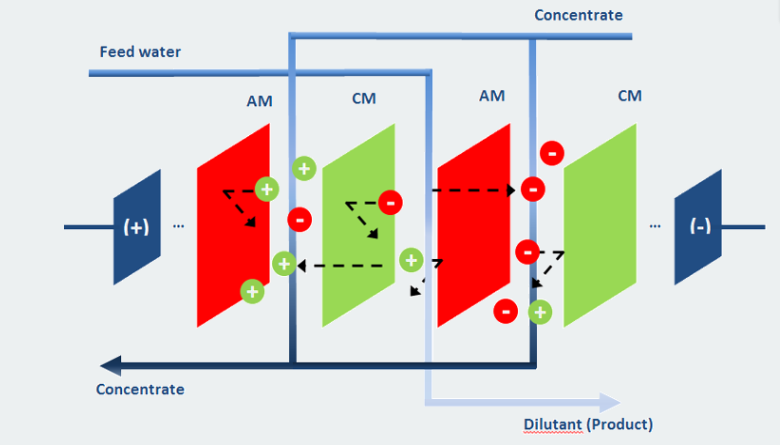
A membrane process that uses an anion selective membrane and a cation selective membrane that are placed between an anion and cation. Electrodialysis reversal system is a membrane process that can effectively treat brackish water. electrodialysis reversal system removed ionized materials from waste water by using a Dc electrical potential and selectively permeable membrane. When an electrical filed is applied the anions move towards the anode and cations move towards the cathode. Cation selective membrane stops the anions and anion selective membrane stops the cations which results in the production of process flow that has low ion concentration and high ion concentration process flow. An electrodialysis reversal system has a cell pair that is a pair of cation selective membrane and anion selective membrane and the areas present between the membranes. An electrodialysis system determines the number of cell pairs in a stack.
| Criteria | Description |
| Status of technology | Has mature and robust technology for desalination of seawater and brackish water. and reclamation of wastewater. |
| Feed water quality bins | Can treat water of all types of chemistry makeup and is also cost effective for removal of total dissolved solids. |
| Product water quality | The quality of water treated depends on the stages of electrodialysis reversal system. Organic pollutants and bacteria cannot be removed. |
| Recovery | 80% product water can be recovered and can also exceed to 90% |
| Chemical use | In order to prevent scaling, acid and scale inhibitor is used. |
| Expected lifetime | 5 to 7 years |
| Infrastructure considerations | There are no special infrastructure requirements only need shed or housing |
| Pretreatment of feed water | Pretreatment of feed water is required to remove scaling and fouling materials |
| Post treatment of product water | Disinfection, demineralization of product water is required |
Table 1: Summary of technical assessment of Electrodialysis Reversal system
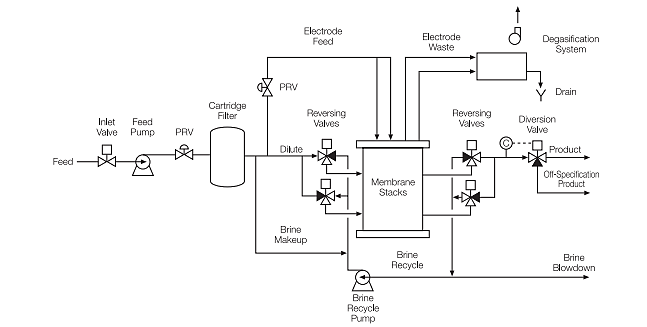

Process function:
In electrodialysis reversal system an electrical field is created by two electrodes that are present on the either side and are submerged in watery salt solution. An electrical field is created around the stack as a result of this. Ion balance is maintained by pumping the salt solution. Ion transport will occur because of the electrical field as the salt solution is also present between the membranes. Between the electrodes, the anions will move to the positive electrode by diffusing through the anion selective membrane and the cations will move to the negative electrode by diffusing through the cation selective membrane. Because the ions leave the dilatant feed and go to the concentrate feed chamber, the concentrations of ions in the dilatant’s cambers of the electrodialysis reversal process decrease. The concentration of anions and cation sin the concentrate chamber increases because the concentrate chamber the anions try to move to the positive electrode but get blocked by the cation-based membrane and the cations try to move towards the negative electrode but get blocked by the anion-based membrane. The direction of ion transport in an electrodialysis reversal system is reversed by reversing the voltage of electrodes every 30 to 60 minutes. This results in the removal of electrically charged particles from the membranes. These electrically charged particles can cause damage and it is recommended to remove them in advance. These particles can be colloid, dispersed particles, humus acids and oils and fats. Membranes for electrodialysis can endure for up to seven years.

Applications for electrodialysis reversal systems include:
- It is used for the removal of charged contaminants from waster. These charge contaminants can be nitrate, chloride, arsenic, radionuclide, fluoride, sulphate etc.
- Electrodialysis reversal system can desalinize ground water as well as surface brackish water.
- Can recover industrial water in semiconductor facilities, O&G extraction and more.
- Electrodialysis reversal system can also remove total dissolved solids from tertiary treated wastewater for irrigation.
- Electrodialysis reversal system can also control ionized contaminants and inorganic constituents in waste water.
- Industrial waste water is desalinated and reused.
- In metal treatment electrodialysis reversal system can recover valuable electrolytes and acids by rinsing baths.
| Industrial applications | Stack and process design | Application Status | Limitations | Key Issues |
| Brackish water desalination | Reverse polarity, tortuous path stack, sheet flow | Commercial | Costs and concentration of feed | Costs and scaling |
| Waste and process water treatment | Unidirectional, sheet flow stack | Commercial | Membrane properties | Membrane fouling |
| Boiler feed water production | Reverse polarity, tortuous path stack, sheet flow | Commercial | Costs, product water quality | Costs |
| Table salt production | Unidirectional, sheet flow stack | Commercial | Costs | Membrane fouling |
| Demineralization of food products | Unidirectional, sheet flow or tortuous path stack | Commercial pilot phase | Costs and membrane sensitivity | Product loss and membrane fouling |
| Concentration of reverse osmosis brine | Sheet flow stack, unidirectional | Pilot phase | Costs | Water disposal |
Table 2: Electrodialysis Reversal system applications in Industry
Benefits:
- High turbidity allowance: High levels of turbidity in feedwater are handled by flowing water through channels along ion exchange membrane surface as electricity moves the ionized salts through membrane.
- Silica tolerance: It flows through the membranes without impacting them as it is uncharged molecule.
- Variability of feeds: Vide variations of total dissolved solids and temperature no significant impact on the process and performance of Electrodialysis reversal system because of its flexibility. Only voltage adjustments are needed.
- Economics of high recovery: Electrodialysis reversal system has low operations costs because supply can be replenished and brie disposal cost is less.
- Reduced pre-treatment requirements: Electrodialysis reversal system requires less pre-treatment as compared of reverse osmosis and provides more robust and reliable operations.
- High salt tolerance: Electrodialysis reversal system uses antiscalant that increases its salt tolerance.
- Low energy consumption.
- High water recovery.
- Less water and chemical consumption.
Disadvantages:
Electrodialysis reversal system has to operate bellow current density limit because diffusion of ions through the membrane doesn’t remain linear to applied voltage beyond particular current density and leads ton water dissociation and decrease in system efficiency. Post-treatment is required for high quality water as electrodialysis reversal system does not remove microorganisms and organic contaminants.
Electrodialysis Reversal System Frequently Asked Questions
1) How is heavy metal removal from industrial wastewater accomplished?
For the treatment of industrial wastewater, trickling filters, stabilization ponds, and activated sludge are frequently utilized. For the most effective removal of heavy metals from wastewater, bio adsorption, a new biological technique, is utilized. Various low cost bio adsorbents (agricultural waste, forestry waste, industrial waste, algae, etc.) are used.
2) How does electro dialysis reversal work?
Applying a DC electric field causes positive ions to flow through cation exchange membranes (CEM) in one direction and negatively charged ions to flow through anion exchange membranes (AEM) in the other. Within a stack, the two varieties of membranes alternate.
3) What is electro dialysis in wastewater treatment?
Ion-exchange membranes are used in the electro dialysis (ED) process to extract ions from aqueous solutions while being driven by an electric current. Like reverse osmosis, ED removes ionic pollutants from water, however current are used as opposed to pressure.
4) What principle is used in electro dialysis?
A selective ion-exchange membrane is used in the electrochemical membrane separation process known as electro dialysis (ED) to transfer ions from one solution to another while being propelled by an electric field (Ghyselbrecht et al., 2013).
5) Which is better reverse osmosis or electro dialysis?
When using ED, lowering energy has no impact on water quality. Even if output is constant, any extra energy is preserved. Regardless of how much salt is removed, RO requires a specific (high) pressure to pump and filter feed water via microscopic membrane holes, ensuring consistent water quality.