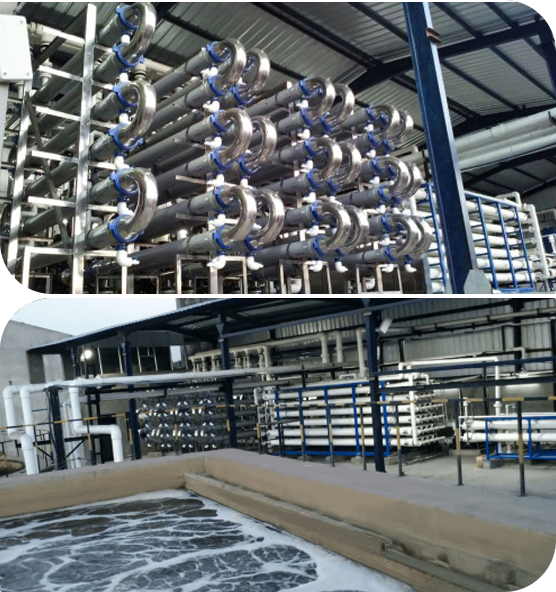
Zero Liquid Discharge System for Textile Industry
Several textile industry companies are using a zero liquid discharge system to recycle textile liquids and wastes. The system uses reverse osmosis and coagulation and flocculation to treat solid wastes and liquids. It is able to remove heavy metals and complex xenobiotic organics from the wastewater. These materials are then reused or recycled to produce new products.
How does Reverse Osmosis Work in Zero Liquid Discharge System?
During the last few decades, reverse osmosis has progressed rapidly. It is now a consolidated process and has been applied to a number of industries, including the dairy and food industries. The technique has also been applied to wastewater treatment for use in industries such as galvanoplasty and paint for metal structures.
A reverse osmosis (RO) process works by pushing water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane. This process is used to separate solutions with different solubility levels. Water molecules pass through the membrane, while larger molecules and ions are blocked. This results in a concentrated water stream.
The flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane reverse when pressure is applied. This creates osmotic pressure, which forces the flow of the more concentrated solution across the membrane.
The ZLD plant features high-pressure trains to pre-concentrate wastewater. The pumps increase pressure on the salt side of the RO membrane.
In the first stage, the water is pumped through the semi-permeable membrane at 80 bars. This results in a reduction in the water content of the brine by at least 40%. The resulting concentrate can be reused in upstream processes. The process also results in 55% less fresh water demand. This water can be reused for irrigation purposes, cooling, and rinsing.
In the second stage, the brine is pumped through seven parallel high-pressure trains to concentrate it by at least 60%. The concentrate is then pumped through advanced membranes. The resulting permeate is clean, allowing the process to be reused for irrigation purposes and other wet processes. It also can be recirculated in production processes to lower energy consumption.
Membrane-based reverse osmosis systems can reduce the operational costs of ZLD/MLD plants. They eliminate the need for thermal processes and other energy-intensive processes. These processes have also been used to reduce the cost of wastewater treatment.
Danfoss is one of the leading companies in the world for high-pressure reverse osmosis pumps. They offer pumps that offer best-in-class performance for pressure requirements up to 80 bar. Their pumps are also cost-effective for the first stage.
What is Coagulation and Flocculation in Zero Liquid Discharge System?
Several dissolved species and suspended particles are removed from wastewater by coagulation and flocculation. Typically, this process is applied before filtration. It can also be applied after sedimentation. However, this treatment process generates a large volume of sludge. For this reason, it is important to select the chemicals and dosing correctly.
During coagulation, a chemical reactant is added to the wastewater. This chemical reactant will be adjusted according to the water’s composition. This chemical reactant will form a gelatinous mass that will trap suspended particles. The gelatinous mass is then stirred to bind metal ions. The metal ions from the anode will then react with hydroxyl ions in the water. This precipitates metal ions into various monomeric species. The precipitated metal ions are then removed by sedimentation or flotation.
The resulting floc is then filtered out of the water. It is usually filtered through a sand filter. This process is used to treat wastewater for industrial applications. The sludge can be recycled as fertilizer for agriculture. However, it is important to note that sludge has high toxicity and should be properly treated.
Coagulation and flocculation is a widely used technique for the treatment of wastewater. Several types of chemicals are used as reagents. These reagents include organic coagulants, mineral coagulants, and flocculation additives. Flocculants include poly-aluminium chloride and anionic polyacrylamide. Polyelectrolytes are also used. These polyelectrolytes act as flocculation agents, superplasticizers, and dispersant agents.
The resulting flocs are slightly larger than the suspended particles. These flocs are also referred to as micro flocs. Because they are small, they are hard to see and can’t be seen with the naked eye. However, they bond to each other, forming larger, more visible flocs. This process is used to filter wastewater.
This process is commonly used in conjunction with sedimentation. However, sedimentation can be replaced by filtration. This process has many advantages. One advantage is that it can remove a large amount of metals. Another advantage is that it is relatively simple. It is also inexpensive.
This process is considered to be the most effective. However, it requires careful planning and maintenance. It is also important to determine the proper concentrations of coagulant and flocculant chemicals. Various studies have been done to determine optimal dosages.
Heavy Metals and Complex Xenobiotic Organics in Zero Liquid Discharge System
Various dyes, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), auxiliary chemicals, and complex organic compounds found in textile manufacturing effluents pose a significant risk to human and aquatic health. These pollutants can harm humans, wildlife, and crops. Effluent treatment systems that eliminate emerging pollutants from industrial effluents are becoming increasingly necessary. However, conventional treatment plants are not well-suited for removing these pollutants. A zero liquid discharge system (ZLD) is a wastewater treatment system designed for the textile industry.
It uses multiple stages of reverse osmosis to remove dissolved solids efficiently. The treated effluent is then reused as process water by textile industries.
The combined effluent of textile manufacturing processes has extremely high total dissolved solids and high organic load. These pollutants can lead to bioaccumulation. The effluent contains traces of heavy metals.
The most important thing to note is that a ZLD textile effluent treatment plant is designed to eliminate emerging pollutants from industrial effluents. Its overall treatment capacity is 4.4 million litres per day, while conventional secondary treated textile effluent is being discharged into natural water bodies.
The ZLD system also uses multiple stages of reverse osmosis and an agitated thin film dryer (ATFD) to remove the dissolved solids efficiently. It is expected that a ZLD plant will contribute to a better water resource recovery from industrial effluent.
Solid Waste by-product of a ZLD System
Various types of chemicals are used by the textile industry. These processes result in production of a large quantity of waste effluent. This effluent contains a number of auxiliary chemicals and dyes. These chemicals can have harmful effects on the environment and the human health.
Industrial effluents are required to be treated to comply with regulations. It is very important to consider the pollution potential of the textile industry before designing a treatment process. The process should include chemical and biological treatment methods.
The textile industry produces a large amount of effluents that are heavily polluted. These effluents can have bioaccumulation and biomagnification. The industry also uses a large number of synthetic fibres and dyes. Therefore, these processes are highly polluting.
The textile industry contributes to depletion of natural resources. Hence, the industry is required to develop a more effective way to treat textile solid waste.
Textile industry is one of the biggest polluting industries in the world. The industry uses a wide variety of chemicals and dyes to produce various kinds of fabrics. These processes generate solid wastes which are either used in the industrial process or discarded. The solids can be reused or sold depending on the quality.
The zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system is used for treatment of waste water. It is an integrated system that includes reverse osmosis and crystallization. This system can be capital intensive, but it can be a great way to reduce the environmental impact of the textile industry. The ZLD system is designed to concentrate potentially hazardous compounds and avoid effluent discharge.
The Bottom Line
The textile industry produces a large quantity of waste effluent that has a high organic load. This means that excessive concentration of dyes in the wastewater could affect the photosynthetic activity of aquatic plants and animals. The high salt content of the effluent can cause adverse effects on the receiving agricultural lands. This use of ZLD system is employed to avoid the toxic discharge of textile effluents.