Smart Effluent Treatment Plants
Introduction
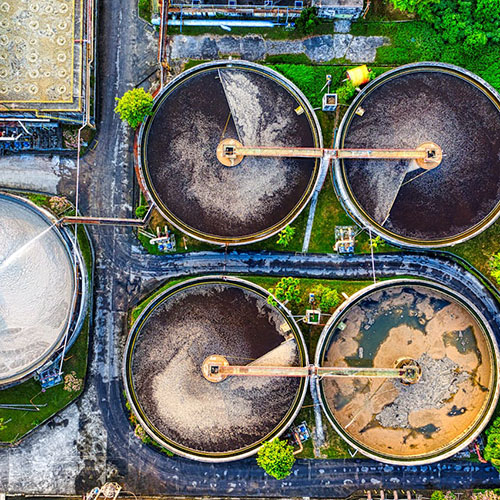
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) are critical for treating industrial wastewater before it is discharged into the environment or reused. Traditionally, these plants operate using pre-defined logic and manual oversight, which can lead to inefficiencies, inconsistent treatment quality, and high operational costs. However, with the integration of smart technologies such as IoT, AI, advanced sensors, and automation, Effluent Treatment Plants can be transformed into Smart ETPs—systems that are intelligent, efficient, sustainable, and compliant.
Key Components of a Smart Effluent Treatment Plant
1. Advanced Sensors & Instrumentation
– pH, TDS, DO, ORP, turbidity, COD/BOD sensors
– Real-time monitoring of influent and effluent quality
– Flow, pressure, and level transmitters
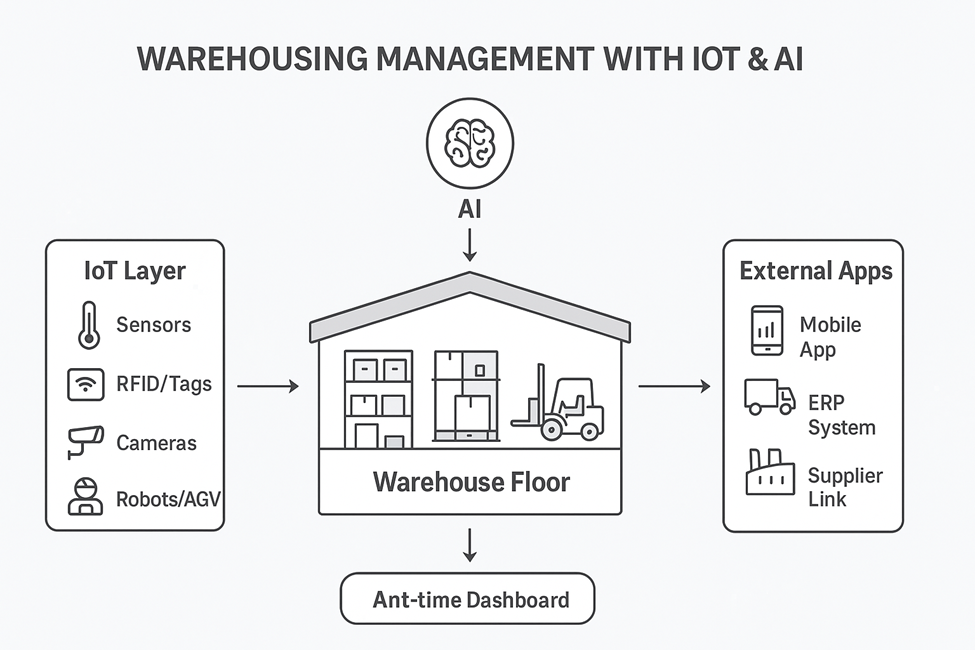
2. IoT Connectivity
– Data from sensors and equipment is transmitted via secure networks to central platforms
– Enables remote monitoring and control of the ETP
3. AI & Machine Learning
– Predictive analytics for maintenance, chemical dosing, and operational optimization
– Anomaly detection (e.g., sudden spikes in pollutant load)
4. SCADA/DCS Integration
– Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) or Distributed Control Systems (DCS) for centralized command and visualization
– Historical data logging, trend analysis, and automated alerts
5. Cloud and Edge Computing
– Cloud platforms for data storage, processing, and remote access
– Edge computing for local real-time decisions without latency
6. Automation and Smart Control
– Automatic backwashing, sludge dewatering, and chemical dosing
– VFDs and PLCs for motor control
Benefits of Smart Effluent Treatment Plants
1. Improved Compliance and Reporting
2. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
3. Energy and Resource Efficiency
4. Predictive Maintenance
5. Enhanced Process Optimization
6. Cost Savings
7. Data-Driven Decision Making
8. Remote Operations and Emergency Response
Applications in Various Industries
– Textiles & Dyeing Plants: Managing high TDS and color
– Pharmaceuticals: Handling complex organic and chemical loads
– Food & Beverage: Biodegradable waste and COD/BOD optimization
– Chemical & Petrochemical: Treatment of hazardous and non-biodegradable compounds
– Automotive & Metal Processing: Heavy metal removal and recycling
Integration with Other Smart Systems
– Smart Water Grids: Treated effluent can be reused in smart irrigation or industrial cooling systems
– Smart Cities: Integrated with city-wide water management platforms for total lifecycle visibility
– Blockchain: For secure logging of compliance data and water reuse credits
Challenges and Considerations
– Upfront Investment: Smart systems are costlier initially but offer long-term savings
– Skill Requirements: Staff must be trained to operate and maintain digital systems
– Data Security: IoT and cloud systems must be protected from cyber threats
– Interoperability: Ensuring that new smart devices can integrate with legacy equipment
Conclusion
Smart Effluent Treatment Plants represent the future of industrial water management. By integrating digital technologies, AI, and automation, these plants offer unmatched operational efficiency, compliance assurance, and sustainability. For industries aiming to meet environmental regulations while cutting costs and improving performance, investing in Smart ETPs is both a strategic and responsible choice.