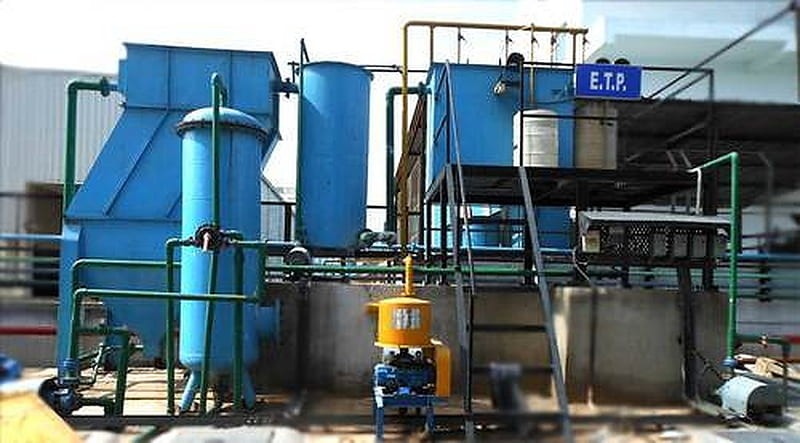
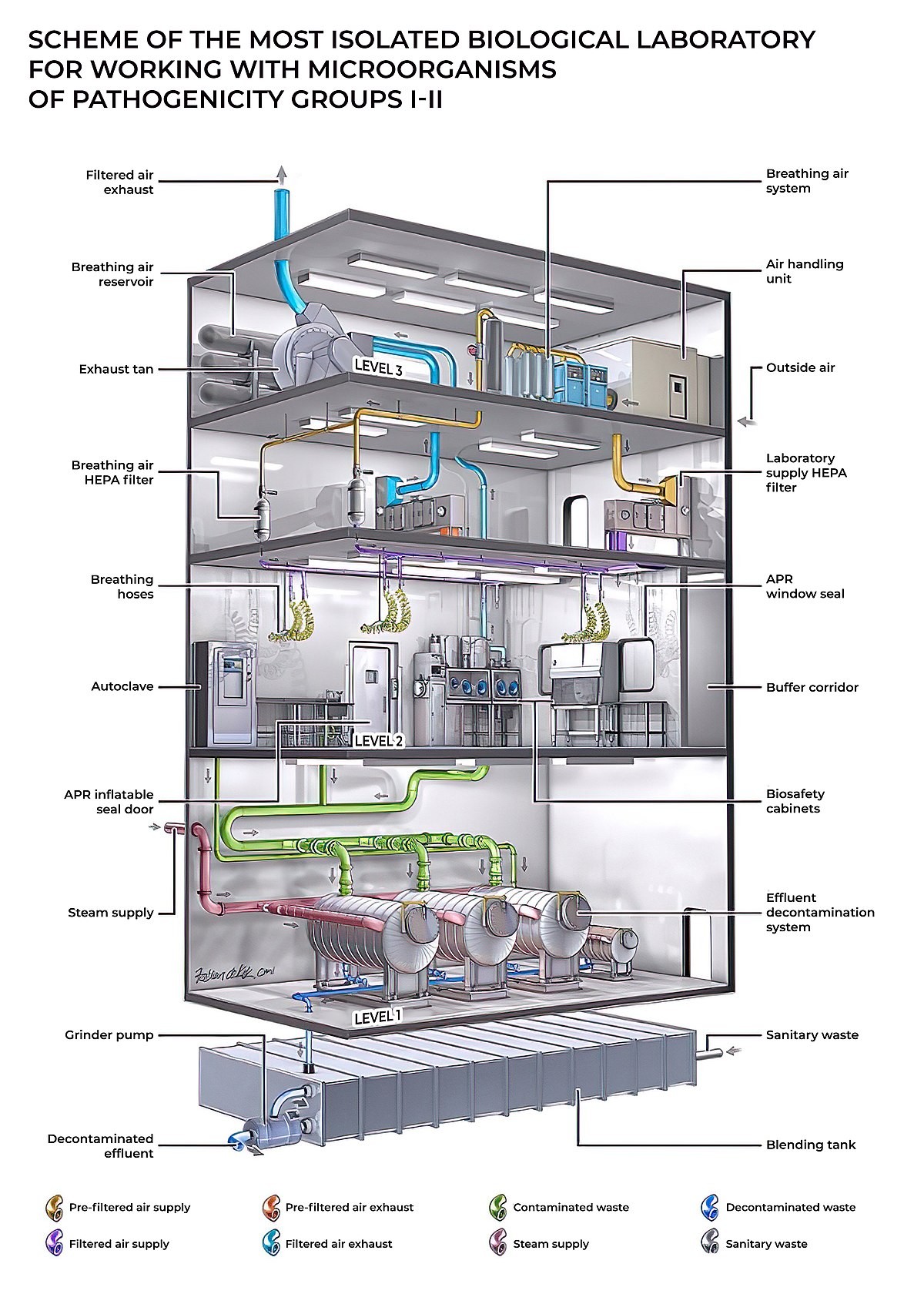
Effluent Treatment Plant in China
An effluent treatment plant is a device that processes sewage, or wastewater. It is an important part of the water and wastewater management industry in China, as it helps to ensure that waste water is treated and discharged in a safe manner. A variety of treatment methods can be used, from mechanical to a biological process. In this article we will look at the different ways of treating sewage.
What are the Benefits of Effluent Treatment Plants in China?
There is a lot of attention being paid to efficient effluent treatment technologies in China. A recent reliable study has summarized the results of 828 wastewater treatment plants in China. The study finds that 89% of the wastewater treatment plants in China are of the mechanical-biological variety, and most of these include a third or fourth stage of treatment.
To improve the performance of the treatment system, some measures have been taken, including the addition of flocculants and process combinations. However, these methods will only be of benefit if they are accompanied by proper management techniques. In this case, the odour, visual colouration, pH and conductivity of the treated effluent should be measured.
One of the major challenges facing downstream treatment plants is the lack of biodegradability. This is especially true for pre-treated pharmaceutical wastewater. It has been shown that a combination of several advanced processes can produce higher biomass concentrations than one process alone.
Several new technologies and approaches have been developed for specific industrial wastewater streams. Among them is the AAO (Automatic Aeration Oxidation) process, which is inexpensive and effective.
Other processes, such as the APMP (Automatic Positively Charged Media) process, have become popular in China. These processes can be a significant upgrade over the existing systems. While they are not as cheap as the AAO process, they are effective enough.
The effluent concentrations of the test plant are lower than those of the reference treatment plant in almost all operating phases. Compared to the literature, the test plant’s effluent concentrations are also comparable. Moreover, the odour, pH and visual colouration of the test plant’s effluent are much better than those of the reference plant.
What is Activated Sludge Process in Wastewater Treatment Plants in China?
An activated sludge process is used in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in China. The method involves the aeration of a mixture of water and biological sludge. This process is commonly used to treat industrial waste waters. However, this process also has its limitations.
The majority of industrial wastewater is treated through activated sludge processes. These processes produce higher quality effluent than other methods of biological oxidation. It is an effective purification technology.
To evaluate the bacterial community diversity of activated sludge high-throughput sequencing was applied. A total of five samples from four different WWTPs were studied. Of the four samples, the richest microbial community diversity was found in the sample from SHZ WWTP. Among the samples, 579 genera and 293 families were identified.
Although the microbial community diversity was richer in the mixed wastewater type, the bacterial abundance in this sample was lower than that in the other types. This could be due to the presence of more easily degradable wastes. Another reason might be the low temperature.
The community diversity was determined using the Shannon’s microbial diversity index, which is based on community richness and diversity (Ace, Chao). In addition, the microbial diversity was assessed by the total number of OTUs observed, which is referred to as the number of shared OTUs.
The abundances of the most abundant phyla were Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Chloroflexi, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. However, a large percentage of the observed OTUs were shared between all phyla.
Furthermore, the study showed that the microbial community diversity in Xinjiang was highly diverse in winter. Therefore, the study is expected to provide more comprehensive knowledge on microbial communities in full-scale industrial WWTPs.
It is important to consider the microbial community diversity in the activated sludge process, and to understand the role of microbes in wastewater treatment. This significant study provides new knowledge and may help to develop efficient solutions for sewage treatment.
An efficient operating solution is necessary for the continuously stricter regulation limits. Activated sludge technology, in combination with complementary treatment, can improve the quality of wastewater.

Discharge Standards of Wastewater Treatment Plant
As industrialization and urbanization proceed, water pollution is increasing in China. A large volume of wastewater is produced, and the resulting effluent has to meet water quality standards. Keeping up with the latest wastewater discharge standards is an important part of China’s efforts to control and mitigate environmental hazards.
For a variety of reasons, the effluent from an effluent treatment plant may not necessarily be the best way to improve water quality. In this case, the most important challenge is to evaluate the effect of the treatment plant on the receiving water body. It is not uncommon for industrial wastewater to contain nondegradable chemicals such as heavy metals and other pollutants, which need to be removed before further treatment. However, the most effective methods of removing these contaminants are usually limited to diluting contaminated industrial wastewater with cleaner wastewater.
The EPA has developed standards for various types of pollutants. These standards are used to determine the minimum requirements for waste water treatment plants. They are designed to protect human health and the environment. This standard includes an indication of the smallest possible concentration of the most common pollutants found in municipal wastewater treatment plants.
Another example is the use of a carbon source from industrial residues. This can be a sustainable option. But the best use of this substance is when it is coupled with other technology and a robust operational strategy. Ideally, the source should be a clean and reliable source.
For example, a focused WWTP that is designed to maintain a required carbon to nitrogen ratio for denitrification is a good place to start. To optimize this process, the addition of sodium acetate is a common practice in China. An alternative approach is the application of a partial bypass of sedimentation.
Finally, it is also possible to implement process engineering to increase the nutrient content of the effluent. However, this would require a greater effort on the part of the treatment plant operator.
Demand from the Municipal Wastewater Treatment Sector
China has been experiencing rapid economic growth and urbanization in recent years. This has led to a high demand for water. In order to address this, the Chinese government has introduced more progressive policies to combat environmental pollution. The wastewater treatment sector has also experienced substantial development in the last decade.
To improve wastewater management, the China government has developed a system of wastewater effluent discharge standards. These standards cover the discharge of wastewater from various industries. As a result, these standards form a standard system of water pollution control in China.
Most industrial wastewater in China is treated in municipal WWTPs. But some industrial wastewater with high organic loads is not easily biodegradable. For this reason, it has to be pre-treated before further treatment. Therefore, the amount of nitrogenous compounds in the discharge standard has been included to reduce nutrient burdens on receiving water bodies.
The Bottom Line
Today, the total number of large WWTPs is around 6.3%. They have treatment capacities of more than 100,000 m3/day. Large WWTPs account for a substantial share of the total wastewater treatment capacity in China.
However, the ratio of treated wastewater to total wastewater has declined in cities. Consequently, the focus has shifted to wastewater treatment in rural areas. Currently, 90 percent of villages in China do not have proper sewerage facilities. Rural communities need affordable treatment facilities. It is estimated that the demand for wastewater treatment in China will be about $19.4 billion by 2025.
With its strong policy support, China has the potential to introduce innovative technologies and to attract foreign investors. In the future, the country will have a wide variety of opportunities to build wastewater treatment facilities in 2nd and 3rd tier cities, as well as for black and odorous water bodies treatment.