An Overview on Desalination Plants in Uruguay Market
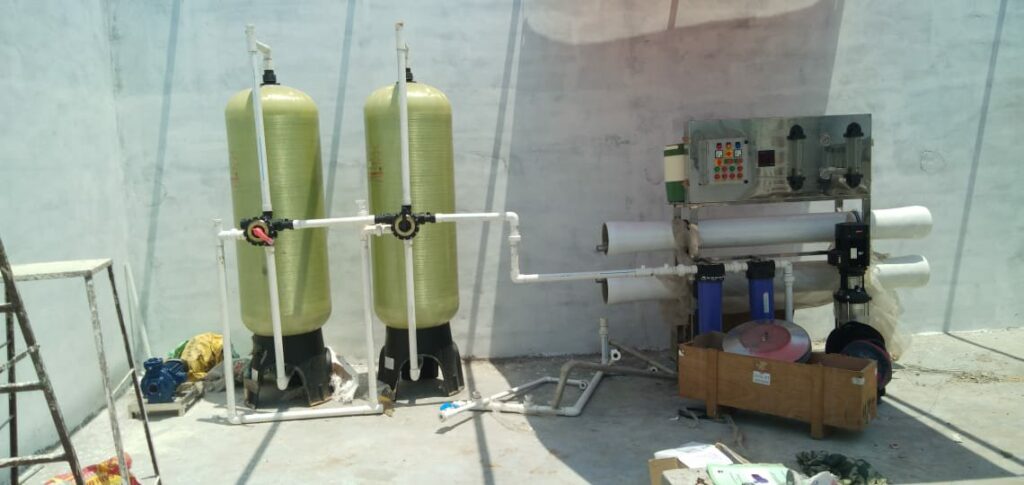
Desalination plants are an important way to treat water in Uruguay. It helps to provide clean drinking water to millions around the world. However, many people are concerned about the environment and the safety of the process. Fortunately, there are many options for safe and effective desalination plants that are available in the market. The following article provides an overview of the industry, discusses its environmental impact, and examines its costs and benefits.
How is the Market of Desalination Plant in Uruguay?
Uruguay is one of the most business-friendly countries in Latin America. In recent years, it has seen foreign direct investment from various countries. This is a testament to the country’s strong institutional framework.
Uruguay’s economy suffered a slowdown, but it rebounded in 2022. The economy grew by 4.4 percent. Its exports and imports reached historic levels in 2022.
Uruguay’s agricultural sector is the base of the economy. Food processing accounts for about half of the industrial production. Agricultural products account for 60 percent of Uruguay’s exports.
Uruguay has a high per capita GDP. Uruguay’s imports were $9.5 billion in 2022. These imports included automobiles, food, and technology. Uruguay also exported goods, including beef and cellulose.
Uruguay’s exports in 2022 grew by 43 percent. China, Brazil, and Argentina were the top export destinations. Exports from the United States ranked fifth.
The country is considered carbon neutral, but it has to contend with energy concerns. Its government has a favorable view of the U.S., which is among the country’s largest trading partners.
Uruguay’s imports and exports are mainly derived from the agricultural and energy industries. Some of the top exports are grain, livestock, dairy, and wood.
How is the Cost of Desalination Plant Determined?
The cost of desalination is determined by many factors. Location, type, technology, application and environmental issues all play a role. These factors must be weighed against each other.
Desalination is a complicated process. It requires a large amount of energy. However, there are ways to cut the cost of desalination. In addition, some companies are using renewable energy to power their facilities.
Increasing the membrane diameter and reducing the amount of water needed for operation can help reduce the energy costs. This can also help reduce the size of the equipment.
Reverse osmosis is an example of a technology that has reduced the energy cost of desalination. A membrane is made up of hollow tubes. The diameter of the tube directly relates to the volume of freshwater that can be desalinated.
Larger plants are able to use renewables for energy. Several regional developers are planning to build plants for power stations.
Water resources around the world are getting more strained by droughts and climate change. More advanced technologies are needed. While these technologies are necessary, their costs are also increasing.
Water treatment systems require post-treatment to destroy viruses and bacteria. Post-treatment is a major cost of desalination.
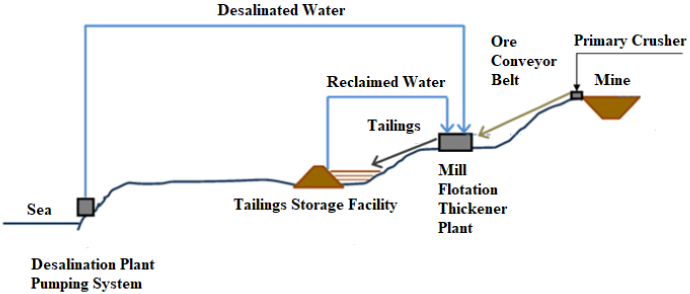
Desalination plants are located close to where communities need water. They are also based near suitable sources of electricity. Some plants are designed to supply up to 100 km inland.
Environmental impact of Desalination Plant
When developing a new desalination plant, it is important to consider its environmental impact. Not only is it important to be aware of the energy and material inputs required, but the plant’s environmental impact on nearby areas should be taken into account as well.
The first step in evaluating a potential new desalination plant is to determine its location and local regulations. If a plant is located near a beach, it might be affected by the ocean’s currents.
Another factor to take into consideration is the environmental impacts of the waste products produced by the process.
In order to reduce the waste product, some plants use a process known as pre-treatment. Pre-treatment is a process where a highly saline solution left over from reverse osmosis is mixed with freshwater. This combination is used in a semipermeable membrane to bind the salt and minerals together. Many desalination facilities are using open ocean intakes. However, some countries are moving toward subsurface intakes, which go beneath the sand.
Private Sector Development of Desalination Plant
Desalination plants are increasingly becoming popular in Uruguay. However, there are some challenges for the industry, including regulatory changes and business model issues. The government is trying to improve the legislation on the industry.
The private sector has been heavily involved in developing desalination plants. A number of companies are proposing new plants, as well as re-submitting plans for older projects. Some of the plants are slated to produce up to 2,000 litres of water per second.
Currently, the mining industry is the main user of desalinated water. Desalination plants can only be built in certain areas of the country. In addition, some communities have environmental concerns. There is a need for transparency in the process, so that concerns can be addressed.
Conclusion
There is no doubt that the global Desalination Plants market is poised for explosive growth in the coming years. With a projected market size of US$2 billion by 2025, there is no dearth of opportunities for players in this industry to snag the best available contracts. A closer look at the latest market scouting reports will reveal that Latin America holds the duopoly in the global Desalination Plants industry. In addition to the region’s rich mineral resources and pristine coastlines, the region is home to some of the world’s most dynamic economies. The resulting influx of technology firms, entrepreneurs and start-ups is expected to catapult the region’s growth, especially in the construction and infrastructure industries.
It’s not surprising then, that the Desalination Plants market has taken a front seat in many of the region’s largest cities such as Uruguay, Buenos Aires, So Paulo, and Rio de Janeiro. Moreover, the presence of a booming industrial and manufacturing sector, coupled with the plethora of research and development centres, has led to the rapid evolution of the industry. As of today, the total number of Desalination Plants stands at roughly 2000, with a projected annual growth rate of nearly 20%. Among these are some of the world’s largest and most advanced plants. Some of the leading countries in the region, such as Uruguay, are investing heavily in the development of Desalination plants in the country.