Challenges and Solutions in Operating Waste Incineration Facilities
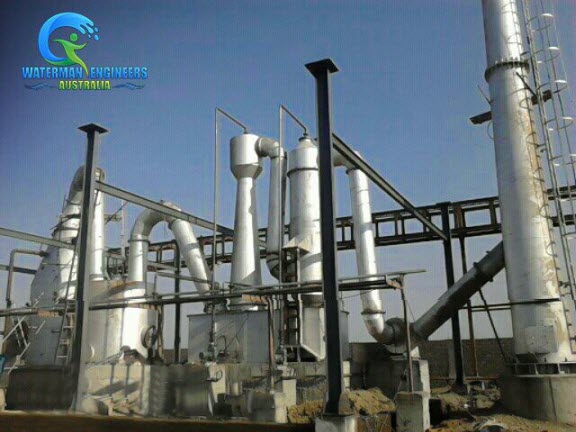
Waste incineration facilities play a critical role in the disposal of solid waste. They provide a means of waste disposal that is safe, efficient, and cost-effective. Waste incineration facilities combust municipal solid waste, hazardous wastes, and other types of waste to produce hot gases and bottom ash residues for disposal or reuse. In addition, these facilities often incorporate other processes for air pollution control and ash handling. These plants can vary in emissions based on the heterogeneous waste mix, the age and type of pollution control equipment, and how well the plant is operated and maintained over time.
However, operating waste incineration facilities comes with its own set of challenges. This article will examine some of the challenges that operators of waste incineration facilities face, as well as potential solutions to those challenges.
Challenges in Operating Waste Incineration Facilities
Emissions in Waste Incineration Facilities
Waste incineration facilities produce various air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, dioxins, and furans, which can harm the environment and pose health risks to nearby communities. These emissions can be harmful to human health, causing respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
To control emissions, operators must ensure that their incineration process is optimized and that they use the appropriate emissions control technologies. These technologies include scrubbers, which remove pollutants by spraying a liquid solution into the flue gas, baghouses, which use fabric filters to capture particulate matter, and electrostatic precipitators, which use electric charges to capture particulate matter.
There are several ways to reduce emissions in the operation of incinerators. One is to install a carbon capture, usage and use storage, or CCUS, on the plant.
Reducing emissions in waste incineration facilities with Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) technology can be an effective solution to the challenges faced by these facilities. CCUS is a process that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes such as waste incineration, and either utilize or stores the CO2 to prevent it from being released into the atmosphere.
Waste Incineration Systems – Waste Composition
Another challenge is the composition of waste. The waste stream is constantly changing, and it can be difficult to determine the best way to dispose of the waste. Different types of waste have different combustion characteristics, and some wastes may contain hazardous materials that require special handling. Waste incineration facilities must handle a constantly changing waste stream that contains a mix of different materials.
Different types of waste have different combustion characteristics, which can affect the efficiency of the incineration process. For example, some waste types may have low calorific values, which means they do not produce much heat when burned, while others may have high moisture content, which can make them difficult to burn. To handle these challenges, operators must ensure that they have systems in place to effectively separate and treat different types of waste.
Energy Efficiency in Waste Incineration Facilities
Waste incineration is the process of burning solid waste to produce steam for electrical energy. This is a relatively new technology that is increasingly being used to reduce the amount of landfill space that is needed for disposal.
Waste incineration facilities generate electricity by converting the heat generated during combustion into steam, which drives a turbine. However, the efficiency of this process can be affected by various factors, such as the composition of the waste, the design of the incinerator, and the maintenance of the facility. To improve energy efficiency, operators can use various techniques such as optimizing the combustion process, recovering excess heat, and using the steam generated by the incineration process for other purposes such as heating or cooling. By doing so, they can reduce the amount of external energy required to operate the facility and lower operating costs.
Maintenance of Water Incineration Facility
Waste incineration facilities require regular maintenance to ensure that they operate efficiently and safely. This includes inspecting equipment, replacing worn or damaged parts, and cleaning the facility. However, maintenance can be costly, and it can be difficult to find qualified personnel to perform the necessary work.
To address these challenges, some operators may choose to outsource maintenance to third-party contractors. Additionally, operators can use condition-based maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis and thermography, to detect potential problems before they occur, which can help reduce maintenance costs.
Training should also be given to those who will be responsible for extinguishing any incidents that do occur. This should be done in conjunction with the local fire brigade to maximise their chances of success.
Solutions in Operating Waste Incineration Facilities
Emissions Control Technologies for Water Incineration
To address emissions, operators of waste incineration facilities can install emissions control technologies, such as scrubbers, baghouses, and electrostatic precipitators. These technologies can capture particulate matter and other pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere, reducing the environmental and health impacts of the facility.
Additionally, operators can use advanced emissions control technologies such as activated carbon injection and selective non-catalytic reduction to further reduce emissions of pollutants such as mercury, dioxins, and furans.
Waste Segregation from Water Incinerator Systems
To address waste composition challenges, waste segregation is key. By separating different types of waste and treating them accordingly, operators can improve the efficiency of the incineration process and reduce emissions. For example, hazardous waste can be treated separately from non-hazardous waste, which can help ensure that hazardous materials are disposed of safely and effectively. Additionally, waste segregation can help operators recover valuable resources such as metals and plastics, which can be recycled or sold.
Energy Recovery Process for Water Incinerator Systems
To improve energy efficiency, operators of waste incineration facilities can focus on energy recovery. This involves using the heat generated during combustion to produce steam, which can be used to generate electricity. This approach can reduce the need for external energy sources and improve the overall efficiency of the facility.
Overall, energy recovery is an important strategy for improving the energy efficiency of waste incineration facilities. By harnessing the heat generated during combustion, these facilities can produce electricity and heat while reducing the need for external energy sources. As technology continues to advance, energy recovery will likely become an increasingly important component of waste management strategies.
Regular Maintenance of Water Incinerator Systems
To ensure that the facility operates safely and efficiently, regular maintenance is essential. This includes inspecting equipment, replacing worn or damaged parts, and cleaning the facility. To reduce costs, some operators may choose to outsource maintenance to third-party contractors.
Operating waste incineration facilities comes with a unique set of challenges. However, by implementing the solutions outlined above, operators can reduce emissions, improve energy efficiency, and ensure that the facility operates safely and efficiently. With proper management, waste incineration can continue to play an important role in the safe and sustainable disposal of solid waste.