Belt Filter for The Treatment of Industrial Wastewater
Belt Filter Overview
In the mining, chemical, and water treatment industries, the belt filter is a type of industrial equipment used in solid and liquid separation technologies such as sludge dewatering. Belt filter presses are used to produce apple juice, wine, and cider. Filtration is mostly achieved by moving a series of filtering cloth or belt through a roller unit.
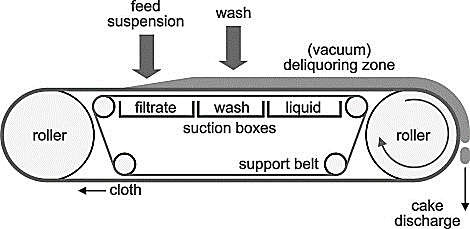 Design
Design
Belt filter designs are created utilizing manufacturer design and quality data, surveys of similar plants, pilot testing, operating installations, and wastewater solids testing in order to achieve a desired dried solid percentage from the slurry or sludge to be treated.
There are the four primary zones of a belt filter press:
- Preconditioning
- Gravity drainage
- Linear compression
- Roller compression
The gravity drainage zone congeals preconditioned sludge, which would be flocculated and coagulated according to the feed and process. The gravity drainage zone would be a flat or sloped belt where free water is gravity drained. The size of the gravity drainage surface is determined by the feed solid concentrations. With the concentrations of solids of 1.5 %, the normal size can be utilised, but for 1.5 to 2.5 percent feed solids, a configuration with a larger drainage basin or extended dimension should be used for greater unrestricted water drainage prior compression.
An independent gravity drainage belt could be employed for dilute sewage with input solids of less than 1.5 percent. This belt has only been utilised in gravity drainage areas. It wasn’t used in pressure zones. The feed is sandwiched between two belts, they are upper and bottom, in the pressure and wedge zones, but each gravity zone does have its own belt, rendering the belt filter the three-belt system. Belt filters can contain additional washing stages, as well as infrared, hot gas, or microwave drying stages, according on the cake’s requirements.
Sludges, slurries, and broken fruit can all be treated with belt filters, which are highly versatile. For a supply or treatment procedure that emits bad smell, volatile emissions, infections, or toxic gases such as hydrogen sulphides. The belt filter may contain fume hoods or be totally encased in a gas-tight enclosure. The belt filter process could also be mechanized due to the limited sight and higher corrosion associated therewith enclosure. Advanced belt press filter designs include large filtration regions, extra rollers, and a variable belt speed.
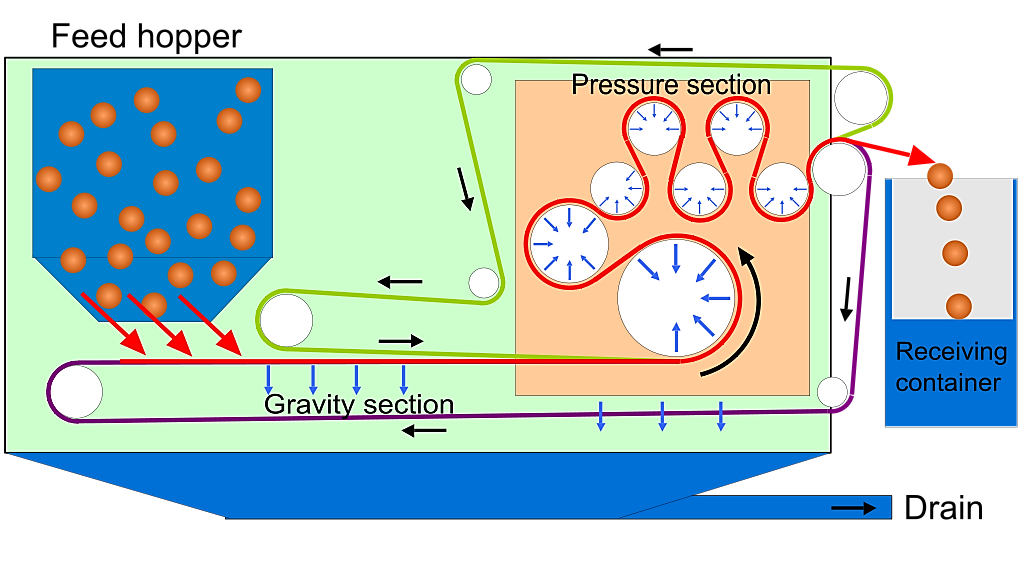 Process Characterization
Process Characterization
But instead of wastewater flow, belt press filters are built for solids capacity. The percentage of primary particles in the feed, as well as any additional solids that may precipitated during treatment, must be determined. The design is anticipated to accommodate varying feed solids concentrations since the content of solids in a process would fluctuate.
The kinds of solids, desired product, and filter design all influence the flow to a belt press filter. The feed solids content is typically of the order of 1-10% for most sludge kinds. The dry solids concentration of the dewatered sludge is usually between 12 and 50 percent. A cake with a lower feed solids concentration has higher moisture content, whereas a cake with an increased feed solids concentration has a better solids filtration rate and a drier final product.
The rate of dry solids input is commonly used as the feed to a belt press filter. Because the incoming solids loading depends on the sludge kind and filter medium, the dried solids loading rate of running belt press filters vary greatly. Reduced range particles loading rates are typically in the 40–230 kg/h/m belt width range, whereas high range solid loading rates are in the 300–910 kg/h/m belt width range. While loading is vital in determining output rate, the depth of cakes formed during the gravity drainage phase must also be considered. The porosity of the filter medium as well as the filtering rate are affected by cake thickness. The ideal cake thickness must be determined through testing for the specific sludge type. It may be required to establish a cake washing phase in some circumstances wherein filtrate recovery is critical.
Necessary Post-Treatment Mechanism
Only in exceptional conditions may a completely clean filtrate be obtained with belt press filters. As a result, additional treatment of the filtrate may be required before it may be recycled or released as waste. If the filter is located downstream of even a clarifier or thickener, the filtrate can be converted back into the clarifier, lowering the needed filtrate clarity and allowing use of more durable cloths. If reusing or recycling the remainder is not a choice, it must be discharged in obedience with the rules and license necessities. Clarified water may require additional treatment before being discharged.
Advantages of Belt Filter
- Belt filter presses can handle a variety of sludge types, including railway, oil, and diatomite-treated wastewater sludge. Some kinds of filter presses can’t process as well as a belt filter press, but it can.
- It is low-cost energy. The belt filter press does have the same effect of the treatment as some other filter presses under same conditions, but it uses 1/3 the water and uses 1/3 the energy of other equipment.
- The belt filter press takes up barely half of the equipment due to its unique design. It delivers the same result as the other filter presses when it comes to treatment.
- The filter belt used with the machine is extremely strong and has a short length. It is difficult to damage because to the unique adjustability construction. The filter belt does have a high durability and performs consistently. In place of traditional carbon steel bearings, high-strength stainless steel bearings have been employed. The equipment’s corrosion resistance has substantially enhanced, and its service life can now surpass ten years.
- The functioning of the belt filter press is also not as difficult as other filter presses due to its basic structure and acceptable design; even regular workers can run it.
- Unlike other filter presses, the belt filter press doesn’t really run on a continuous basis. The belt filter press can run for up to 24 hours on a single charge.
Disadvantages of Belt Filter
- It’s appropriate for sludge with high moisture content.
- Maintenance is a challenge.
Belt Filter Wastewater Treatment Frequently Asked Questions
1) What is Belt Filter?
A common piece of industrial equipment used in solid-liquid separation processes, such as sludge dewatering in the water and wastewater treatment industries, is the belt filter. The most popular filtering technique involves passing a series of filtering belts or cloth through a roller unit.
2) What is the purpose of a belt filter?
Water is removed from liquid wastewater residuals using belt filter presses, which creates “cake,” a non-liquid substance. Dewatering wastewater solids improves operation, lowers costs for further storage, processing, transfer, end use, or disposal, and decreases the volume of residuals.
3) What are the types of filter systems?
Mechanical, biological, and chemical filtration are the three basic forms of filtering.
4) What equipment is used for wastewater treatment?
Water contaminants can be neutralized and removed using technology such as reverse osmosis systems, ultrafiltration systems, vacuum evaporators and filters, paper bed filters, solid bowl centrifuges, and tramp oil separators.
5) How do you purify industrial wastewater?
Advanced Oxidation Processing, distillation, adsorption, nitrification, incineration, chemical immobilization, or landfill disposal are some of the available techniques. A modified method of wastewater treatment can be applied when a substance, such as some detergents, is capable of biological breakdown.