Rotary Drum Screens in Hydropower Plants
Rotary Drum Screens for hydropower plants, which are widely used for fish protection and debris/moss removal at turbine intakes.
⚙️ Rotary Drum Screens in Hydropower Plants
🔎 What is a Rotary Drum Screen?
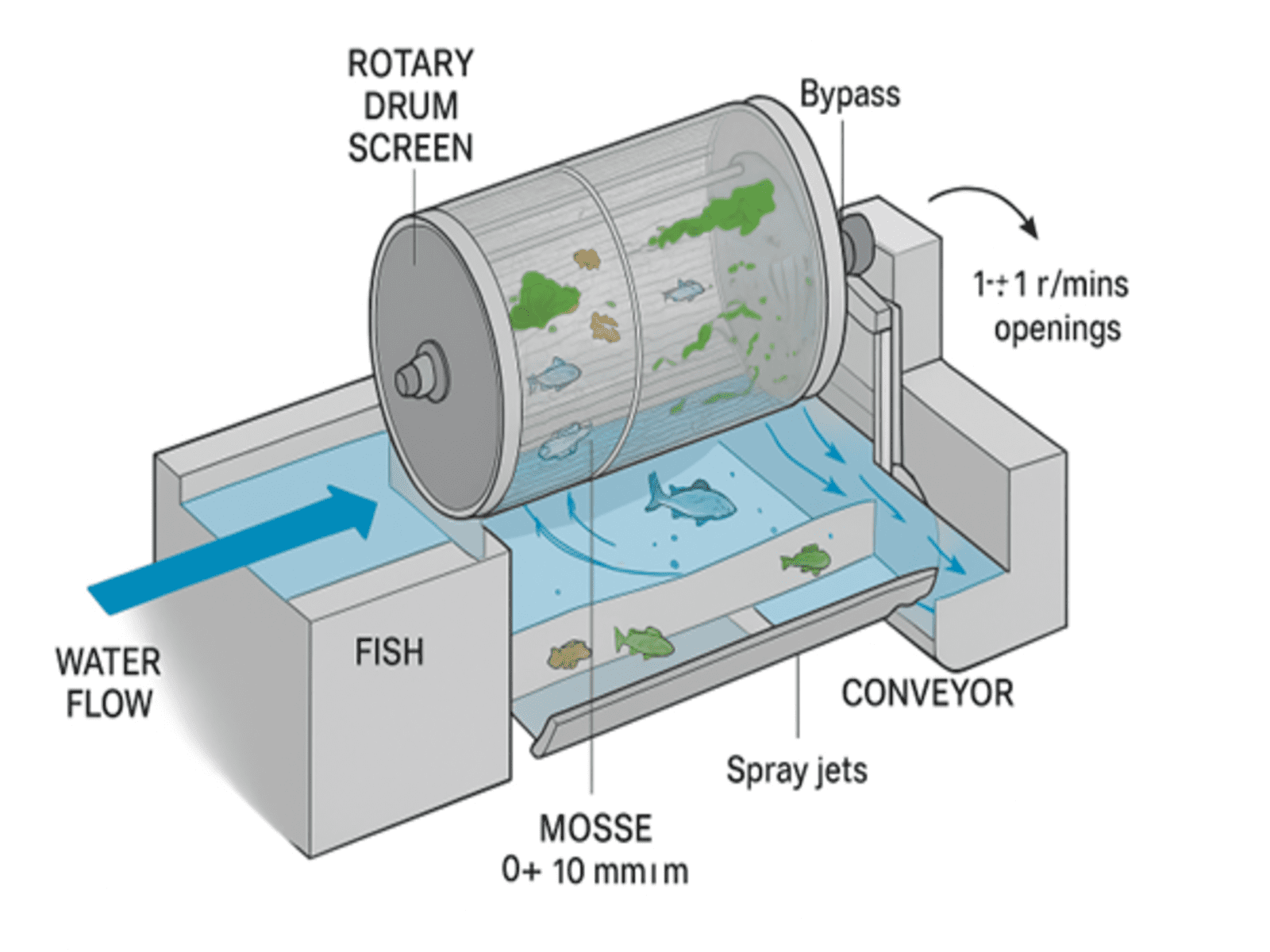
A rotary drum screen is a cylindrical drum with fine mesh or wedge-wire panels that rotates slowly in the water intake channel. Water passes through the screen into the intake → fish, moss, and debris are blocked and guided to a bypass → clean water enters the turbine.
Working Principle
- Water Flow
- Water enters the drum’s submerged portion.
- Screen mesh (slots 1–10 mm depending on target species) allows water through but blocks fish and debris.
- Fish Guidance
- Fish encounter the rotating drum surface.
- Flow and rotation guide them to a bypass channel alongside the drum.
- Self-Cleaning
- As the drum rotates upward, spray jets or brushes clean off trapped moss, algae, and debris.
- Waste is collected in troughs and conveyed away.
📏 Design Features
- Drum Size: Large diameter (2–6 m typical) and width up to several meters.
- Screen Material: Stainless steel wedge-wire or perforated mesh.
- Slot Size: Fine openings (1–2 mm for juveniles, 6–10 mm for larger fish).
- Rotation: Slow (1–5 rpm), powered by water current or motors.
- Bypass Location: Adjacent to drum for easy fish entry.
🐟 Role in Fish Protection
- Prevents fish from being drawn into turbines.
- Guides fish gently to bypass with low stress and high survival (>95%).
- Especially effective for juvenile salmonids, smolts, and eels, which follow surface flows.
🌱 Role in Moss & Debris Removal
- Removes floating moss, algae mats, and leaves before they clog penstocks.
- Continuous cleaning system reduces downtime and labor.
- Maintains hydraulic efficiency of intake flow.
✅ Advantages
- High fish protection efficiency (meets US NOAA / EU WFD standards).
- Automatic self-cleaning → low manual maintenance.
- Handles large debris + fine moss
- Long lifespan (stainless steel construction).
- Works in variable water levels and flows
⚠️ Limitations
- High capital cost compared to fixed bar screens.
- Needs reliable power or flow for drum rotation.
- Requires spray water system for cleaning.
- Performance depends on correct approach velocity design (≤ 0.3 m/s for juveniles).
🌍 Example Applications
- Columbia River (USA): Rotary drum screens protect juvenile salmon downstream of dams.
- UK Small Hydro Plants: Used for eel and trout protection at intakes.
- Norway & Germany: Installed for both fish safety and algae removal in alpine rivers.
✅ In summary:
Rotary drum screens are self-cleaning, rotating fish protection and debris removal systems at hydropower intakes. They ensure safe fish bypass, prevent turbine clogging from moss/algae, and maintain continuous operation with minimal manual cleaning.
Excellent request 👍 Let’s compare Rotary Drum Screens and Traveling Water Screens, since both are widely used in hydropower intakes for fish protection and debris/moss removal.
🔄 Comparison: Rotary Drum Screen vs. Traveling Water Screen
| Feature | Rotary Drum Screen | Traveling Water Screen |
| Basic Design | Large cylindrical drum (2–6 m dia.), rotates slowly in water. | Vertical conveyor-like screen with mesh panels attached to chains, moving upward and downward. |
| Screen Surface | Continuous curved drum surface. | Flat panels moving vertically. |
| Operation | Water flows through drum → fish/debris blocked → fish guided to bypass → debris washed off by spray jets. | Water flows through vertical screen panels → debris lifted out of water → high-pressure sprays remove debris at deck level. |
| Self-Cleaning | Automatic via drum rotation + spray jets. | Automatic via moving panels + spray wash at top. |
| Fish Protection | Very high survival (>95%). Fish gently guided to side bypass. Best for juvenile salmonids, eels. | Effective if approach velocity ≤0.3 m/s. Fish lifted away from intake but sometimes exposed to mechanical stress at spray wash. |
| Debris & Moss Handling | Excellent for moss, algae mats, floating debris. Drum keeps continuous removal. | Good for large debris (sticks, trash, leaves). Less effective for fine moss/algae unless frequent cleaning. |
| Bypass Integration | Direct lateral bypass channel adjacent to drum. | Fish bypass chute or sluice integrated near screen face. |
| Energy Use | Low (slow rotation, only spray pumps). | Moderate (continuous chain drive + spray pumps). |
| Maintenance | Simple, fewer moving parts. Long life (stainless steel drum). | More moving parts (chains, sprockets). Higher mechanical wear. |