Photocatalytic Degradation of Waste Water In Textile Industry
Introduction
Photo catalyst degradation is generally defined as a method in we use photo catalyst that is able to activate a reaction without being used. These photocatalytic substances are mainly invariable.
There are lot of technologies that we used for the treatment of waste water i.e. Electrodialysis, membrane filtration, precipitation, adsorption, electrochemical reduction, and electrode ionization. These wastewater recovery techniques may be efficient but consume large amount of energy and generate pollutants, various type of hazardous waste and by products during the treatment of waste water treatment that have adverse effect on our environment. According to economic and social point of view we need mild reaction conditions and effective catalysts to remove various contaminants from wastewater. Scientist discovered a technique of Heterogeneous photo catalysis. This technique used in a variety of fields, including water splitting, water/air purification, CO2 reduction, and nitrogen fixation.
Photo catalysis, is a simple and environmentally friendly process. It can degrade organic contaminants present in textile effluents into water, carbon dioxide, and particles. It also decreases or convert harmful inorganic pollutant into less hazardous chemical
Principle
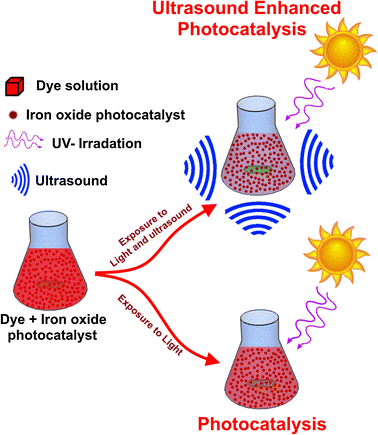
The stimulation of photo excited electron-hole pairs with adequate energy (equal to or greater than the band-gap energy) at start in a photocatalytic process. The little gap in photo catalyst is able to capture light with more visible photon. In second step the dissociation of photogenerated electrons and holes occur. The creation of phonons or heat produced when the majority charge carriers recombine. It results in a decline in the amount of stimulated electrons. Electrons and holes both engage in a variety of reactions. These charge carriers are mix on the surface. Furthermore, they also react with oxygen to form superoxide ion that produce OH ions as well. The pollutants present in water are first deposited on the surface of the catalyst. It enhances charge transportation and redox reaction ability. Then a sequence of chemical changes starts happening with active specie. These active species produced by catalyst to produce degradation products. Photo-Fenton process is a so-called process similar to photocatalytic activity that can occur. The formation of extra OH radicals from Fenton reagents occur in this process.
Photocatalytic Reactor Design
Within photocatalytic water treatment sector, photocatalytic reactors are particularly essential. Identifying the appropriate reactor can help to speed up treatment process while also saving electricity. Because light is used as the process energy with in photocatalytic reactor, the utilisation efficiency of the source of light as well as the mass transfer effectiveness of illumination in the reactor must be evaluated. The catalyst’s placement in the reactor will maximize the area of contact, catalytic efficiency, reaction rate, and photocatalytic reaction efficiency. As a result, developing a novel photocatalytic reactor is a crucial approach to speed up the practical use of photocatalysis.
As per the type of catalyst used, photocatalytic reactors are classified as
- Fluidized Bed Reactors
Catalysts are put directly just on granular carriers immersed in the fluid to be processed in fluidized bed reactors. They have a wide surface area, low mass transfer constraints, and a quick reaction velocity, however the catalyst is hard to retrieve and agglomerates easily, causing obstruction, making industrial amplification problematic.
- Fixed Bed Reactors
Whereas the fixed bed reactor does have a smaller surface area than that of the fluidized bed reactor, it is easier to distinguish the catalyst from of the liquid, and the catalyst could be recycled, therefore it has a bright future in industry.
Preparation of Photocatalyst
By Chemical Method
The solution-based method is a widely used method for making photocatalysts since it has multiple benefits, including being eco-friendly, having inexpensive chemicals, and requiring very little energy input. The efficiency of the manufactured photocatalyst can be regulated by altering the operating settings. Various compositions, forms, and dimensions could occur from the variables used in the design phase, which could alter the photocatalyst’s effectiveness. As a result, as contrasted to a solid-based method, this method is preferred. Some of its examples are:
- Sol-Gel
- Co-Precipitation
- Electro-spinning
- Hydrothermal
By Physical Method
The use of a machine, pressure, power, and force to mix or modify the structure of materials, such as sonication, solid-state, and thermal evaporation, is prevalent in the synthesis of photocatalysts utilizing physical techniques. When compared to chemical-based procedures, these technologies have various advantages, including straightforward technical features and a highly pure yield. Nevertheless, controlling the catalyst’s structure, size, and composition is difficult. One of the devices that may be used to synthesize the photocatalyst utilizing acoustic energy is a sonication bath. The ultrasonic probe emits ultrasonic waves with varying power pressures, capabilities, and structural forms. Various products will be achieved with various amplitude, frequencies, power supply, and processing time. This substance also has a high potential for producing a quality product with a high yield and minimum waste from of the procedure which is beneficial in textile industry.
Specific Beneficial Catalysts for Textile Wastewater Treatment
Some beneficial catalysts for textile wastewater treatment are:
- Titanium dioxide
- Zinc oxide
In photocatalytic degradation of genuine textile industry water, titanium dioxide and zinc oxide revealed to be really effective catalysts. Within 150 minutes of irradiation, ZnO achieved 64.41 percent decolorization and TiO2 achieved 95.29 percent decolorization at 37 degree Celsius and pH of 9. The greatest decolorization was 90.48 percent at pH 7.3. The fact that decolorization occurs at lower pH supports the idea that pH is one of the most critical operating parameters affecting the catalyst’s photocatalytic reactivity. When TiO2 was mixed with H2O2, the highest decolorization was around 86 percent, but it happened in less than 50 minutes. Titanium dioxide has a faster reaction rate than other metals. The findings show that TiO2 is much more beneficial than ZnO in treating genuine textile wastewater.
Advantages of Textile Wastewater Treatment
This method has a number of benefits:
- It is environmentally friendly treatment.
- Total pollution degradation is held in this process.
- Certainly, no secondary pollution.