Market for Desalination Plants in Chile
The water scarcity in Chile has threatened the production of copper. In order to meet this demand, several companies are looking for the construction of desalination plants. However, there are some concerns with the use of desalination plants in the Atacama Desert. These concerns are discussed in this article.
How Water Scarcity Threatens Copper Production in Chile?
Despite being the world’s leading copper producer, Chile is experiencing a water crisis. The country has been faced with a seven-year drought, which is forcing large mining companies to reduce production. This has particularly affected the rural population.
The drought has irreversibly damaged crops. It has also prompted farmers to sell their land and move into cities. These changes have been exacerbated by record high temperatures. There are several factors contributing to the current water shortage, including natural and anthropogenic factors.
In northern Chile, the arid region is experiencing the highest water scarcity. The aquifers in this area are fragile and susceptible to overexploitation. While some operations are already using desalination, it is not always feasible.
Nevertheless, the Chilean government is looking to tackle the water crisis. A national strategy has been developed to promote the efficient use of water. To do so, the government is establishing a forum to boost coordination.
Currently, there are two major water sources in southern Chile: rainfall and seawater. Despite having high average water runoff availability, the two sources are highly unequal.
In addition, the mining industry has been using water from underground aquifers for decades. Eventually, these sources will be exhausted.
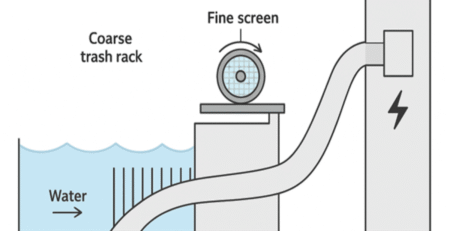
Desalination plants are one of the potential solutions to the Chilean water crisis. However, they are expensive. They are also not usually feasible in the high Andes. This could have an impact on the copper market.
Copper mining in Chile requires a lot of water. The copper mines are pumping water from underground aquifers. Hundreds of rural communities have been forced to sell their land.
What is the Cost of Desalination Plants in Chile?
The costs of desalination plants in Chile have been growing in recent years. These plants are designed to help local communities and mining firms by supplementing their water supply. However, there are several factors that affect the cost of desalinated water.
One of the main issues is the availability of high cordillera water for many projects. This resource is not available in areas that are far from the coast.
In addition, energy costs are associated with pumping water up into the high cordillera. It is also important to understand the potential for electricity subsidies.
Desalination plants can be designed to work with solar farms. For example, if the solar resource is low, the grid can take over. When solar resources are plentiful, the plant can use energy storage.
Desalination plants are a great advance towards ensuring potable water. However, they are not without political and social impacts. Depending on your input data, the cost of desalinated water can vary.
There are four key elements in a supply chain. The first component is the desalination plant itself. Another component includes pipeline pumping. Finally, there are other capital costs such as land, design, and permitting.
As a result, the final cost of water is highly sensitive to the assumptions and methods used. A simple model enables calculation of the daily production, daily energy, and daily water cost. Similarly, the cost of energy is determined by different power sources.
The first large-scale desalination plant in the country was built in the year 2003. Today, it supplies more than 150 lps of potable water.
Growth of Desalination Plant Market in Chile
The Chilean market for desalination has witnessed significant growth in recent years. This is due to a wide range of factors. From climate change to water scarcity, the country is facing numerous environmental concerns.
Desalination is a process that uses high-energy processes to purify water. This results in water suitable for human consumption. Moreover, this industry is a good way to supplement local water supplies and relieve pressure on natural water sources. However, the industry poses many other environmental concerns.
An Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is one of the most important legal instruments in Chile. Its purpose is to evaluate the effects of a given project. In the case of a desalination plant, the EIA focuses on specific effects, mainly relating to the socio-economic aspects of the project.
The first evaluation in the country was completed in 1997. Since then, the duration of environmental assessments in the country has increased.
Brine production from the desalination plants has also grown significantly. According to estimates, the installed production capacity is currently about 6,000 litres per second. This is projected to double by 2032.
Currently, the largest users of consumptive water in Chile are the agricultural sector and the mining industry. During the period between 2020 and 2022, the average daily output of desalination for industrial purposes was about 1.26 Mm3/day.
Impact of Desalination Plant in the Atacama Desert
Desalination plants in the Atacama can play an important role in helping address the water crisis. However, the process of processing desalinated water is expensive.
Desalination plants in the region can also help reduce the climate change impact on groundwater. It has been estimated that Atacama Desert electricity generation could supply 20% of the world.
The Atacama Desert is a unique place. Not only because of its geographical and climatic characteristics, but also because of its unique vegetation.
The Bottom Line
Desalination plants are a dime a dozen these days, and their role in the economy is growing fast. According to estimates, the installed production capacity will reach approximately 6,000 litres per second by the end of the year. This is a significant step in the direction of ensuring potable water to a thirsty populace. The government is also taking steps to encourage the efficient use of scarce resources. In addition to desalination plants, the country is also looking to boost local economic dynamism by promoting the development of low-cost concrete and low-wage local labour.