The Role of Activated Carbon in the Recovery of Precious Metals from Effluent
Effluent is wastewater from industrial processes that often contains hazardous chemicals, including precious metals. These metals are valuable resources that can be extracted and reused through an effective recovery process. Activated carbon is a highly effective and widely used material in the recovery of precious metals from effluent.
Activated carbon is a natural adsorbent that can be made from many different raw materials. It is produced through either thermal (physical/steam) activation or chemical activation.
It is a porous material with micropores that act as an attractive force for the adsorption of impurities. It can be used for a variety of applications in industries and households.
The extraction of precious metals from wastewater requires a highly efficient and cost-effective method. Activated carbon is a highly porous material that is capable of adsorbing a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds. This unique property makes activated carbon an ideal choice for the recovery of precious metals from wastewater.
What is Activated Carbon?
Activated carbon is a highly porous material that is made from carbon-rich sources, such as coconut shells, wood, and peat. The carbon source is heated in the absence of air to produce a highly porous material with a large surface area. This surface area allows the material to adsorb a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds, including precious metals.
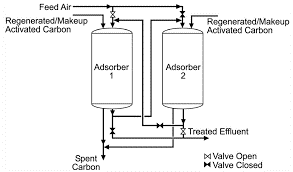
How Does Activated Carbon Work?
Activated carbon works by adsorbing contaminants onto its surface. The highly porous structure of activated carbon provides a large surface area for adsorption to occur. The contaminants are attracted to the surface of the activated carbon and are held there by Van der Waals forces. The adsorption process is reversible, which allows the precious metals to be recovered from the activated carbon through a desorption process.
The Role of Activated Carbon in Precious Metal Recovery
Activated carbon plays a crucial role in the recovery of precious metals from effluent. The adsorption process is highly effective in removing precious metals from wastewater, and the desorption process allows for the recovery of these metals in a highly concentrated form. The recovered metals can then be reused, reducing the need for new mining operations.
Precious Metal Recovery from Effluent
Precious metals such as gold, silver and platinum are used in a wide range of products including jewellery, electronics and industrial applications. These metals possess many characteristics such as oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, strong electrical and thermal conductivity, flexibility, and catalytic activity.

The effluent containing these precious metals is often funnelled through sewage treatment plants, where it ends up as sludge. This could present an opportunity for the recovery of gold and other valuable metals.
Activated carbon can play an important role in the recovery of precious metals from effluents. It has been shown that CC-8×30, a granular activated carbon, can be used to selectively absorb gold and other metals from dilute chloride solutions.
The Versatile Applications of Activated Carbon Adsorption
Activated carbon is a unique adsorbent, prized for the extremely porous structure that allows it to effectively capture and hold materials in liquids or gases. Activated carbon is used in a wide range of applications that require the removal of undesirable elements from liquids or gases.

Depending on the source material, activated carbon can be produced through either thermal (physical/steam) activation or chemical activation. Either process enlarges the carbon’s pore size, increasing its internal surface area and making it more accessible to adsorption by the molecules in the solution.
The pores in activated carbon have a variety of sizes, called micropores (small), mesopores (medium) and macropores (large). This is important because it affects the amount of adsorption that can occur. For example, small molecules such as chlorine are adsorbed more in carbon with micropores than they are in carbon with macropores. Adsorption of color molecules such as phenols and tannins is also influenced by the size of the pores in the carbon.
Importance of Activated Carbon in Precious Metal Recovery
Activated carbon is one of the most effective adsorbents used to recover precious metals. It is also widely used in air and water purification.
ACTIVATED CARBON is manufactured from a variety of raw materials. These include waste sulfite liquors, lignin from wood and petroleum products, and waste lubricating oil.
The raw material is heated and then treated to produce activated carbon. During the heating process, steam is added to aid in opening up the pores.
In chemical activation, several chlorides are added to the raw material before it is heated. During this process, the chemicals bind with the carbon to create the active carbon.

Activated carbon has been used for over a century for severalsss industrial applications. It is a good adsorbent for various impurities and pollutants. It has a high surface area-to-volume ratio and is very porous. It is an important adsorbent material for the recovery of gold and silver from effluents.
Activated Carbon in Wastewater Treatment
In the world of wastewater treatment, activated carbon plays a critical role in the removal of heavy metals. It is an ideal adsorbent for this application, as it has a large surface area per unit volume (see illustration below).
The adsorption capacity of raw materials such as coal or charcoal may be sufficient for useful applications, though further chemical treatment often enhances adsorption properties. Activated carbon is produced by heating carbonaceous material such as coconut husk, peat, wood or lignite to a temperature that binds the particles together and creates an impermeable carbon layer. Activated carbon can be found in various forms including granular and powdered.