Precious Metal Recovery as a Solution to the Problem of Resource Depletion
As our planet’s populace burgeons and our technological capabilities advance, the exigency for natural assets is amplifying at an unprecedented pace. A number of these resources, particularly those of the precious metal classification, are becoming exceedingly scarce as a result of their overuse and depletion. However, with the advancement of technology and innovation, we can use precious metal recovery to solve this problem.
From electronics to medical equipment, precious metals play a vital role in the production of many products. Due to their rarity, these metals are becoming increasingly scarce, which poses a significant problem for the future.
What is Resource Depletion?
The depletion of natural resources, an issue that greatly impacts the economy, environment, and society at large, pertains to the complete exhaustion of these resources. Such depletion of resources, including metals, minerals, and fossil fuels, occurs primarily as a result of overuse, which leads to augmented demand and prices. This overuse leads to depletion, which results in scarcity, making it difficult to meet the growing demand.
The Importance of Precious Metal Recovery
The recuperation of precious metals is a technique that encompasses the retrieval and reprocessing of these metals from discarded materials. This procedure provides multiple advantages, including the curtailment of mining, the preservation of natural resources, and the minimization of waste. By extracting and recycling precious metals, not only are energy and resources conserved, but the alleviation of environmental contamination is also achieved.
The Process of Precious Metal Recovery
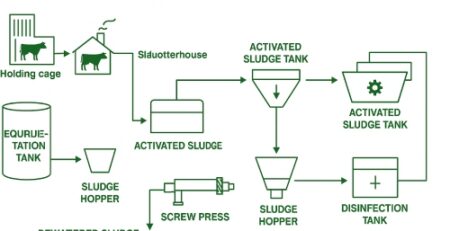
The recuperation of precious metals involves various methods, including pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy and bio metallurgy. Pyrometallurgy, one such method, employs high temperatures to extract metals from discarded materials. Hydrometallurgy, on the other hand, involves the use of chemicals to extract metals from waste. Bio metallurgy is a process that involves the use of microorganisms to extract metals from waste.
Applications of Precious Metal Recovery
The application of precious metal recovery is vast and varied. One of the most significant applications is in the electronics industry, where precious metals are essential in the production of electronic devices. The automotive industry also relies heavily on precious metals for the production of catalytic converters, which help to reduce emissions.
The future of precious metal recovery is promising, as more companies and organizations are adopting this process to reduce waste and conserve resources. With the advancement of technology and innovation, we can expect to see new and more efficient ways of recovering precious metals from waste.
Benefits of Precious Metal Recovery
The benefits of precious metal recovery are numerous. This process helps to conserve natural resources, reduce waste, and reduce the need for mining. The extraction and recycling of precious metals also help to mitigate environmental pollution, making it a sustainable solution to the problem of resource depletion.
Challenges of Precious Metal Recovery
While the process of precious metal recovery is beneficial, it also comes with some challenges. One of the most significant challenges is the cost of the process, which can be expensive, especially for small businesses. Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure and technology in some regions, which makes it difficult to adopt the process.
The problem of resource depletion is a significant issue that affects the world’s economy, environment and society. Precious metal recovery is a sustainable solution to this problem, as it helps to conserve natural resources, reduce waste, and mitigate environmental pollution. While the process of precious metal recovery comes with some challenges, the benefits far outweigh the costs.
Precious metal recovery is a solution to the problem of resource depletion because it reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. The process starts with recycling electronic equipment waste, which is then smelted to separate the metal from the other materials in the waste.