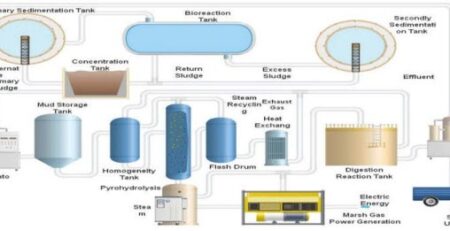
Key Roles and Techniques of Filtration by Pharma Grade Water Plant
Pharma Grade water plants are used to filter water by various types of filtration system which are used in pharmaceutical industry. It is easy to operate with minimum maintenance.
Key Roles of Pharma Grade Water Plants in pharmaceutical industry
Water is a vital ingredient in the pharmaceutical industry. It plays a key role in the processing, formulating and manufacturing of APIs and pharmaceuticals. It also needs to meet stringent hygienic requirements. For example, it must be clean, pure and of the right quality for sterile applications.
There are several ways to purify water. One way is through microfiltration, which involves the use of fine particles to remove suspended solids and other contaminants. Another method is through the use of ultrafiltration, which uses a combination of different filters to eliminate suspended matter.
It’s also possible to make water using electrolysis, a process that involves applying high voltage to a solution of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen. This process produces extremely pure water that can be used for a variety of purposes including pharmaceutical production.
Investing in the right pharmaceutical grade water system is a critical step towards ensuring a safe and healthy work environment. You need a reliable system that delivers consistently high-quality water, delivered at the right flow and temperature to meet your pharma processes’ requirements. The pharma grade water plant by Waterman Australia can fill all these needs.
Achieving this requires a comprehensive approach that includes the latest in microbiological technology and equipment. This includes an effective system design and control strategies to minimize the impact of microbiological growth, reduce the risk of cross-contamination and ensure the safety of workers.
Various Techniques for Filtration by Pharma Grade Water Plant
There are several methods to ensure that water used in pharma facilities is safe. One is to use UV disinfection, which is a relatively cheap but effective way of eliminating pathogens in water. Other techniques include filtration, ionisation, reverse osmosis, and distillation.
In addition to ensuring that the water quality is safe, it is also important that the process of producing it is controlled in order to ensure that any contamination is detected early on and removed before it can cause a problem. This can be achieved by using a system that monitors the flow of water, ensures that the water is not contaminated with microorganisms or other contaminants, and that the process is controlled.
The efficiency of these processes can vary, and it is therefore essential that they are properly designed and operated to achieve their intended outcomes. Optimisation of the electrode geometries, the reactor configuration and the operating parameters are all important considerations.
Types of Water for Pharma Grade Water Plant
Water quality is a vital factor in the pharmaceutical industry and water purification technologies are used to ensure that the water meets strict quality standards. There are four grades of water in pharma manufacturing: potable (mains) water, purified water, highly purified water, and water for injection or WFI. Each grade of water has unique microbial issues and requires different methods of treatment to ensure that it is safe for use in the production and delivery of drugs.
The main goal of water treatment is to remove the chemical contaminants that could pose a threat to human health and the environment, including pharmaceutical compounds. Some of these toxins can be removed by various oxidation and deconjugation processes. Others can be removed by membrane filtration.
Pharmaceutical water systems are critical for microbiological control, and a variety of design and control measures are needed to keep them safe from contaminants. The most important criteria for a safe pharmaceutical water distribution system is the ability to minimize standing water, which can increase microbial contamination and decrease the aesthetic quality of potable water. This is achieved through the use of sanitization systems that are placed at each point in the system and a strategy for reducing microbial growth through regular maintenance and sanitation activities.