In-Depth Technical Elaboration on IoT and AI for Theft, Robbery, and Leak Prevention in Utility Supply Systems
In-Depth Technical Elaboration on IoT and AI for Theft, Robbery, and Leak Prevention in Utility Supply Systems
1. Internet of Things (IoT): The Sensory and Communication Backbone
1.1 IoT Sensor Types and Functions
- Flow Sensors: Measure instantaneous and cumulative volume of fluid (water, oil, gas) passing through the pipeline or distribution point.
- Pressure Sensors: Monitor pressure levels upstream and downstream, key for detecting abnormal drops indicating leaks or ruptures.
- Acoustic Sensors: Detect sound/vibrations caused by leaks or mechanical tampering.
- Temperature Sensors: Abnormal temperature changes can hint at leaks, blockages, or tampering.
- Vibration and Motion Sensors: Detect unauthorized physical disturbances or tampering near pipelines or meters.
- Cameras and Drones: Visual monitoring at critical points, integrated with motion detection.
1.2 Communication Infrastructure
- LPWAN Protocols: LoRaWAN, NB-IoT for low-power, long-range data transmission from meters and sensors.
- Mesh Networks: Each IoT node relays data from neighbors to the gateway, increasing robustness.
- Cellular & Satellite: For remote or mobile pipeline segments.
- Edge Gateways: Preprocess sensor data locally, provide initial filtering and response.
1.3 Data Acquisition and Security
- Continuous or periodic sensor data collection.
- Encrypted, authenticated data transmissions.
- Secure firmware to prevent IoT device hacking.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI): From Data to Intelligence and Action
2.1 Data Analytics and Machine Learning Models
- Anomaly Detection Models:
- Statistical Models: Establish baseline flow, pressure, temperature patterns; detect deviations.
- Supervised Learning: Train classifiers (SVM, Random Forest) on labeled data of known leak/theft events.
- Unsupervised Learning: Clustering and outlier detection to flag new, unseen anomalies.
- Deep Learning: LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) networks for time-series analysis to predict unusual events.
- Predictive Maintenance Models:
- Use historical sensor data to predict equipment failure or degradation.
- Schedule proactive repairs to avoid leaks or meter malfunctions.
- Behavioral Analytics:
- Profile normal customer or pipeline section consumption.
- Identify irregular usage indicating theft or illegal tapping.
2.2 Real-Time Decision-Making and Automation
- AI systems analyze data streams in real-time, scoring each event’s likelihood of being a leak or theft.
- Alert Generation: Automated alerts sent to operators or maintenance teams.
- Automated Actuation: Integration with valves and shutoff mechanisms for automatic isolation of affected pipeline sections.
Dynamic Resource Allocation: Prioritize field crews based on AI-assessed severity and location.
3. Specific Use Cases: Theft, Robbery, and Leak Prevention Mechanisms
3.1 Theft Detection via IoT + AI
- Unusual Flow Patterns: AI flags sudden drop to zero or sharp increase inconsistent with historical consumption.
- Flow Reversal Detection: Some meters can detect flow direction; reverse flow can indicate bypass or tampering.
- Pressure Anomalies: Unexpected pressure changes near customer premises often indicate illegal tapping.
- Tamper Sensors: Detect opening of meter boxes or physical meter damage.
- AI Behavioral Models: Continuously learn and update normal usage patterns, flagging suspicious deviations.
3.2 Leak Detection and Localization
- Pressure Gradient Analysis: IoT sensors measure pressure at multiple points; AI calculates expected pressure drops and flags abnormal losses.
- Acoustic Leak Detection: Microphone arrays and AI analyze sound signatures to detect and locate leaks with high precision.
- Flow Imbalance: Comparison of inlet vs outlet flow in pipeline segments highlights losses.
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Detect moisture or temperature changes indicative of underground leaks.
3.3 Robbery Prevention
- Video Analytics: AI analyzes camera feeds for unauthorized access attempts.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Motion and vibration sensors trigger immediate alerts.
- Geofencing and GPS Tracking: Track pipeline inspection and maintenance vehicles to prevent internal theft or sabotage.
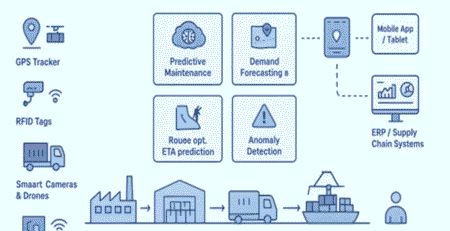
4. Architecture and Data Flow Example for Leak/Theft Detection System
[IoT Sensors] –> [Edge Gateway / Local Processing] –> [Cloud Platform & AI Engines] –> [Operator Dashboard & Alerts]
| | | |
|—- Data Preprocessing |—- Anomaly Detection Models —-|— Real-time Alerts ——-|
| | | |
|—- Immediate Valve Control (actuation) <—————–|
- IoT devices measure and transmit data.
- Edge gateways filter noise, perform initial threshold checks.
- Cloud AI models analyze trends, detect anomalies.
- Operators receive alerts and visualized analytics.
- Automated valves can shut off sections immediately upon critical alerts.
5. Benefits and Impact of IoT + AI in Theft and Leak Prevention
| Benefit | Description |
| Rapid Detection & Response | Early leak/theft detection reduces water/oil loss and environmental damage. |
| Reduced Operational Costs | Automated monitoring reduces manual inspections and emergency repairs. |
| Improved Revenue Protection | Detects theft quickly, reducing financial losses. |
| Enhanced Safety & Environmental Protection | Quick leak isolation prevents accidents and contamination. |
| Optimized Maintenance Scheduling | Predictive analytics avoid costly unexpected failures. |
6. Practical Examples and Industry Implementations
- Oil & Gas Pipeline Monitoring: Companies use IoT flow and pressure sensors combined with AI platforms like Microsoft Azure or AWS IoT Analytics to detect leaks within seconds.
- Municipal Water Utilities: Smart meters integrated with AI leak detection reduced non-revenue water by up to 30% in pilot projects.
- Cross-Border Gas Pipelines: Real-time AI analytics on IoT sensor data enable remote monitoring of sensitive international pipelines with immediate alerting on sabotage or illegal tapping.
7. Challenges and Advanced Solutions
| Challenge | Advanced IoT + AI Solutions |
| Sparse Sensor Deployment | AI uses data interpolation and models to estimate conditions in unmonitored segments. |
| Data Quality & Noise | Edge AI performs real-time data cleaning and noise filtering. |
| Cybersecurity Threats | AI-based anomaly detection identifies unusual network traffic or device behavior. |
| Scalability | Cloud AI platforms handle millions of sensor inputs with distributed processing. |
8. Summary
- IoT provides the physical sensing and communication capabilities to continuously monitor pipelines and distribution networks.
- Artificial Intelligence analyzes this massive, high-frequency data to detect leaks, theft, and tampering early and accurately.
- Together, IoT and AI enable automated, real-time protection of pipeline infrastructure, saving costs, protecting resources, and enhancing safety.