The Future of Waste Incineration: Innovations and Advancements
Waste management is one of the most significant environmental issues of the 21st century. The increasing amount of waste generated by the world’s growing population has become a serious concern, as traditional waste management methods are not sustainable in the long run. In this regard, waste incineration has emerged as a promising technology that can efficiently and effectively deal with waste. However, the use of incineration has been controversial, with concerns about pollution and emissions. In this article, we will explore the future of waste incineration, including innovations and advancements that promise a greener and more sustainable approach to waste management.
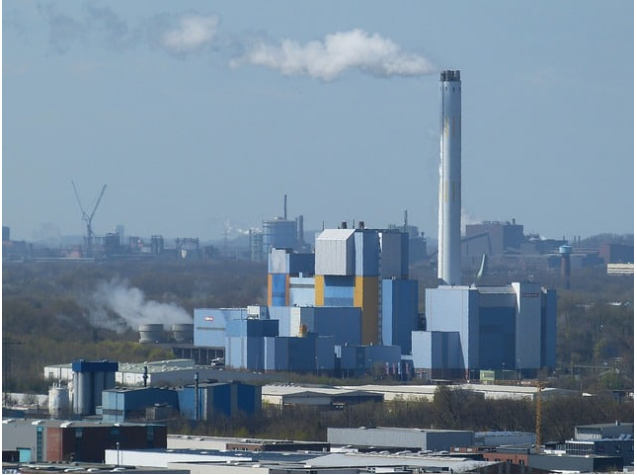
Incineration is a waste-to-energy (WTE) process that turns solid waste into electricity and/or steam. It’s one of the oldest technologies used for recycling, but it has seen many innovations and advancements.
The main benefit of waste-to-energy is that it reduces the volume of waste that must be landfilled. But it does not completely remove the need for landfills, so communities will continue to need them in the future.
Innovations in Waste Incineration
To make waste incineration a greener and more sustainable option, several innovations have been developed in recent years. One of the most significant innovations is the development of advanced combustion systems, which can increase the efficiency of the incineration process while reducing emissions. These systems use advanced technology to optimize the combustion process, resulting in cleaner emissions and reduced energy consumption. Another innovation is the use of waste-to-energy plants, which convert waste into energy that can be used to generate electricity, heat, and fuel. These plants are becoming more common worldwide and are a crucial step towards sustainable waste management.
Advancements in Waste Incineration
Advancements in waste incineration technology have also led to the development of new waste management methods. One such method is the use of plasma gasification, which uses high temperatures to convert waste into a gas that can be used to generate electricity. This process has several advantages, including the ability to handle a wide range of waste types, reduced emissions, and the production of a clean gas that can be used as a fuel. Another advancement is the development of carbon capture and storage systems, which capture carbon dioxide emissions from the incineration process and store them underground. These systems can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from waste incineration, making it a more sustainable option.
Addressing Concerns about Waste Incineration
Despite the benefits of waste incineration, concerns about pollution and emissions remain. However, advancements in technology have addressed many of these concerns. For example, advanced combustion systems and waste-to-energy plants have reduced emissions significantly, making waste incineration a cleaner and more sustainable option. Additionally, the use of carbon capture and storage systems can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, waste incineration is a heavily regulated industry, and emissions are strictly monitored to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Carbon Dioxide Capture for Emissions Reduction in Waste Incineration
One of the more intriguing technologies that could be applied to waste incineration is Carbon Dioxide Capture. This technology, which is also known as carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS), is used to reduce emissions by removing carbon dioxide from industrial facilities before it has a chance to enter the atmosphere.
The process involves capturing and then transporting carbon dioxide to geological storage sites, where it is stored long term. There are several different ways to do this, including piping it through injection wells deep underground where the CO2 is locked away permanently.
Another option is to compress and chill the CO2 and then pipe it through pipelines. However, these pipelines are expensive to build and require high pressure and low temperatures to maintain.
Additionally, the CO2 needs to be transported to a storage site that can handle it safely. There are several possible sites, but some of them include oil and gas reservoirs and deep saline formations.
While there are several potential carbon capture technologies, it is unclear how these technologies will help decarbonize waste incineration in the future. Until more research is completed, it is unclear whether this technology will be able to deliver the required level of emissions reduction in time to meet net-zero goals for waste disposal.
Waste Incineration with Energy Recovery
Energy recovery from waste is a powerful solution that reduces landfill waste, increases energy security and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Instead of burning fossil fuels, waste is dried and combusted in a controlled airflow environment. The heat generated is converted into steam which drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Incineration with energy recovery is a growing waste management strategy that can reduce waste volumes in landfills and create economic benefits for communities. The process involves several steps, including burning wastes, converting waste to ash, and extracting energy from the ashes for use in local power grids.
The process is also a great way to recycle a portion of the waste stream that would otherwise be sent to a landfill. For example, food waste can be burned to recover valuable nutrients and generate energy that can be sold back to the community.
In some cases, the resulting energy can be used to provide hot water or space heating. In other cases, the heat is used to drive a turbo-generator that transforms the waste into electrical energy, which can be sold to local utilities. As the world becomes more aware of its environmental impact, it is important to keep in mind the many ways that energy recovery can help protect our planet.
Advancements in Fuel Utilization and Emission Control for Waste Incineration
One of the key technologies to make waste incineration more efficient is to increase the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), which is a measure that shows how efficiently an incinerator turns energy into heat and electricity. In the past, AFUE has typically been lower for waste incinerators than for those that use conventional fuels like natural gas and oil. However, there are advances in fuel utilization technology that are making it possible for incinerators to turn waste into more valuable products, such as liquid fuels and carbon dioxide gas while minimizing energy requirements.
Another way to boost fuel utilization is by upgrading conventional oil and natural gas into more valuable products, such as synthetic diesel or methanol. These can be dispensed with as a by-product of industrial processing or marketed for other uses.
A fourth way to improve fuel utilization is by reducing emissions from incineration plants. These include a variety of technologies including CO2 capture, fuel storage, energy recovery and emission control.
Innovations and Advancements will be crucial to ensure that waste incineration can continue to help solve our planet’s growing waste problems. It will also contribute to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and global warming, while also helping to create jobs and boost economies.