Electrolysis Treatment for Hazardous Waste
What is Electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the process of producing a chemical reaction by the flow of an electric current through a substance or mixture of substances, often in liquid form. Therefore, electricity is the flow of electrons or ions. For electrolysis to work, the compound must contain ions. Electrolysis is the process of decomposing a substance. It often decomposes the compound into its components. To perform electrolysis, two electrodes, called the positive electrode and the negative electrode (cathode), are submerged in the electrolyzed material and connected to a source of direct current. The device that performs the electrolysis is called the electrolytic cell.
The fluid conducts electricity because its positive and negative ions are free to move, the positive ions towards the cathode and the negative ions towards the anode. This transfer of a positive charge in one direction and a negative charge in the opposite direction creates an electric current because the electric current is, after all, only the flow of charge, and it does not matter whether the carriers of the charge are ions or electrons.
Electrolyte
If an electrolyte is needed, a substance must be able to conduct electricity. A fluid that contains both positive and negative ions and is therefore capable of conducting electricity. An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, allows electricity to flow through the solution. Electrolytes promote this flow because they produce positive and negative ions when dissolved. During electrolysis, current flows through the solution in the form of positive ions (cations) that move to the negative electrode and negative ions (anions) to the positive electrode.
Working mechanism of electrolysis
During electrolysis, the ions move towards the electrodes of opposite charges. When they reach their electrodes, they experience chemical oxidation and reduction reactions. This is what happens during electrolysis:
- At the cathode, which pumps electrons into the electrolyte, the chemical reduction captures the electrons through the positive ions.
- At the anode that removes electrons from the electrolyte, chemical oxidation causes the electrons to be lost by the negative ions.
In electrolysis, there is a direct relationship between the amount of electricity flowing through a cell and the amount of chemical reaction that occurs. The more electrons pumped through the electrolyte by the battery, the more ions will have to give up electrons or lead to oxidation or reduction. To produce a chemical reaction like that of a mole, a mole of electrons must pass through a cell. One mole of electrons, i.e. 6.02 × 1023 electrons. This is called Faraday.
Applications
Hydrogen Production
Electrolysis is considered an environmentally friendly way to produce hydrogen. Photo electrolysis, in which photovoltaic particles contain electrolytes that decompose water into hydrogen, and oxygen gas can be used to produce hydrogen. It mainly divides water into hydrogen and oxygen and supplies it to various industries. These technologies can be used to store hydrogen, which is converted into electricity in fuel cells when a natural energy source is not available. Locally high purity hydrogen and oxygen supply have the advantages of producing hydrogen at small facilities, and hydrogen production by electrolysis has minimal impact on the environment.
Waste recovery
It is usually a recycling technology that recovers useful resources from waste. It is mostly used in electrolytic cells to separate precious metals and organic compounds from waste. Electrolytic cells are designed to reduce certain types of waste. In this regard, microbial electrolysis cells can be a suitable example of combining biological and chemical waste reduction methods to ensure better yields of recovered resources. Such cells are still in evolution technology that has the potential to regenerate hydrogen gas, biofuels and other organic compounds.
Electrolysis of Water Principle
The core of the electrolysis unit is an electrochemical cell, consisting of two electrodes filled with purified water and connected to an external power supply. At a certain voltage, called the critical voltage, between the two electrodes, the electrodes begin to produce hydrogen gas at the negative bias electrode and oxygen gas at the positive bias electrode. The amount of gases produced per unit time is directly related to the current travel through the electrochemical cell.
Working mechanism
Water electrolysis is considered a well-known method to produce oxygen and hydrogen gas. Pure water does not conduct electricity well, it must be made into an electrolyte by dissolving acid, base or salt. Then, an anode and cathode, usually made of a non-reactive metal such as platinum, are inserted and connected to the power connection. At the cathode, electrons are pumped into the water by a battery, which is taken up by water molecules to form hydrogen gas. At the anode, electrons are removed from the water molecules. Each of the two water molecules is divided into two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The acid, base or salt that converts water into an electrolyte is selected so that its specific ions are not oxidized or reduced, so they do not react chemically and only maintain the current flow through the water.
Production of magnesium
Oceanic water is the main origin of the metals, which have more magnesium ions in them than any other metal besides sodium. First, magnesium chloride is acquired by bringing out the magnesium hydroxide from oceanic water and dissolving it in hydrochloric acid. Then, magnesium chloride was liquefied and electrolyzed. Like the production of sodium from the above-dissolved sodium chloride, the dissolved magnesium is deposited at the cathode, while chlorine gas is released at the anode.
Electroplating
One of the most important uses of electrolysis is electroplating. The process of electroplating is coating a cheap conductor with metal is called electroplating. This is done for protection or decoration. Electroplating produces a thin coating of metals (silver, gold, chromium and nickel) on the surfaces of cheap metals to provide the appearance and chemical resistance of precious metals.
Silver cyanide is used in the electrolyte instead of other silver compounds such as silver nitrate in silver electroplating because the cyanide ion combines with the silver ion to generate the complex ion Ag (CN)2. This limits the supply of free Ag+ ions in the solution, so they accumulate only slowly at the cathode. It creates a dazzling, long-lasting silver coating. Gold plating is done in the same way as using gold anode and electrolyte gold cyanide.
Purification of copper
Unlike other metals like aluminium, copper is chemically easy to acquire from its ores. But it can be refining up to 99% by electrolysis. Pure copper is important in the manufacture of electrical wire because the electrical conductivity of copper is reduced with impurities. These impurities contain precious metals such as silver, gold and platinum, when removed and recovered by electrolysis, go a long way in paying the electricity bill.
By the electrolytic treatment of copper, impure copper is prepared in the electrolyte bath of copper sulphate and sulfuric acid from an anode. As current flows through the solution, the positive copper ions in the solution are attracted to the negative cathode, where they pick up electrons and deposit themselves as neutral copper atoms, allowing more pure copper at the cathode. Meanwhile, the copper atoms in the positive anode release the electrons and dissolve copper ions in electrolyte solution. Meanwhile, the copper atoms release electrons at the positive anode and dissolve the copper ions in the electrolyte solution. However, the impurities at the anode does not go into the solution because the silver, gold and platinum atoms are not oxidized as easily as copper. So silver, gold and platinum fall from the anode to the bottom of the tank only where it is scraped.
Making of sodium hydroxide
Caustic soda is another name for sodium hydroxide. It is the most important of all industrial chemicals. The main method of making it is the electrolysis of salt, saline solution and sodium chloride in water. Chlorine and hydrogen gas are produced as valuable by-products. When an electric current goes through saltwater, the negative chloride ions go to the positive anode, lose their electrons and turn into chlorine gas. Sodium ions, at the same time, are drawn to the negative cathode. However, it does not take electrons to convert into sodium metal atoms, as in dissolved salts. This is because the water molecules in the aqueous solution receive electrons more easily than the sodium ions. Hydroxide ions, together with sodium ions already in solution, form sodium hydroxide, which can be recovered by evaporation.
Advantages
- Electrolysis is widely used in the metallurgical industry, in processes such as the extraction of metals from ores and the refining and deposition of metals from solvents.
- Electrolysis is used to purify certain metals such as copper and zinc.
- Chlorine can also be prepared by electrolysis of some common saline solutions. In submarines, the oxygen produced by the electrolysis of water is used for respiration.
- Electrolysis is used to electroplate many objects that we use every day. Metal impurities can be effectively removed by electrolysis. The solution prepared by electrolysis protects the metal from corrosion.
- It is also used to produce alkaline earth metals and alkali metals from their salts such as sodium chloride, which can be broken down into elements such as sodium and chlorine.
- Electrolysis makes metal attractive and gives it a neat appearance. Electrolysis is usually applied for the coating of one metal with another. Easily corrosive metals are protected by a coating of non-corrosive metal. Nickel and chromium plating are widely used in the automobile industry.
- Hydrogen is also produced by the electrolysis of water, which has a wide range of applications in the industrial field. It has great advantages for locally producing hydrogen at small facilities to supply high purity hydrogen and oxygen and can be used as an energy source for hydropower.
- In addition to the nuclear system process, it is very easy to dispose of nuclear waste that leads to nuclear power generation. Because it is simply dumped in a geographical location where it will deteriorate over time and have no negative impact on the environment.
- It is also very useful for making heavy water, for example deuterium oxide used in nuclear reactors is also made by water electrolysis.
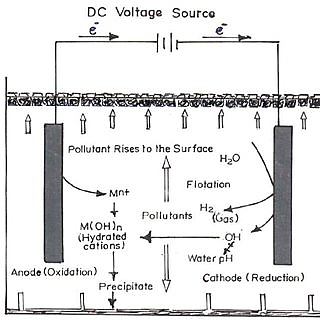
Pollutant to be treated by Electrolysis
Electrolysis is one electrochemical wastewater treatment technology. Electrolysis technology is a necessary and complex process that involves many chemical and physical phenomena in many areas of wastewater treatment, including clean synthesis, monitoring of contaminant removal efficiency, sterilization of water, clean energy conversion and efficient storage and electricity consumption. Electrolysis has important advantages such as its simple equipment, convenient operation and the absence of the need for chemicals for sedimentation and flock production. This allows wastewater treatment to be oxidized electrochemically or to reduce organic contaminants to non-hazardous inorganic substances. The main processes that occur during electrolysis are electrolytic reactions at the electrode surface, the formation of clots in the aqueous phase, absorption of soluble or friction contaminants and removal by sedimentation and flotation.
To purify drinking water, halogen pills are commonly used. When the halogen tablet is dissolved in water, chlorine ions are produced, which are strong oxidizing agents. This basic idea of high toxicity and bacterial oxidation of chlorine ions was attempted to assess the effect of hydroxyl ions produced by electrolysis on bacteria, bacteria. When the water container undergoes electrolysis, hydroxyl and hydronium ions are produced, which move from one electrode to another through the fluid. These ions, especially the hydroxyl ions, will come across bacteria and react chemically with them to remove them. This process is similar to the mechanism for disinfecting water using a halogen table. Electrolysis allows recycling to begin by removing salts from this water. The driving force is provided by the electric field applied by the electrodes. It uses removes the chloride content in the water to eliminate the chlorine water.
Electrocoagulation technology has many advantages over conventional coagulation. First, it is more effective at destabilizing small friction particles. Second, it can achieve simultaneous freezing and flotation with low sludge production. Third, the devices are very compact and therefore suitable for installation where space is limited. Electrochemical treatment appears to be the best treatment method due to its high effectiveness, low maintenance cost, low labour requirement and rapid achievement of results. Electrolysis relatively is simple equipment, oxidation or reduction chemistry and the potential advantages of operation at ambient temperature and pressure.
Electrolysis Treatment Frequently Asked Questions
1) What is electrolysis in wastewater treatment?
The electrochemical wastewater treatment method of electrolysis is currently becoming more and more common and technologically advanced. It is an intricate process involving numerous chemical and physical phenomena that adds ions to the wastewater using disposable electrodes.
2) What are four methods for disposing of hazardous wastes?
Alternative ways for treating hazardous waste include chemical, thermal, biological, and physical processes. Incineration, chemical neutralization, and land farming are a few examples.
3) What happens during the process of electrolysis of water?
When water is exposed to electric current, it undergoes electrolysis, which breaks down the liquid into oxygen and hydrogen gas. When an electric current is delivered across a water molecule, the water molecule breaks down into the ions H+ and OH-.
4) What is electrolytic treatment?
The electrochemical wastewater treatment method of electrolysis is currently becoming more and more common and technologically advanced. It is an intricate process involving numerous chemical and physical phenomena that adds ions to the wastewater using disposable electrodes.
5) What is electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment?
Anodes and cathodes, two pairs of metal sheets used in electrocoagulation, are placed in pairs of two. The cathode is oxidized (loses electrons), while the water is reduced (gains electrons), using the principles of electrochemistry to improve the treatment of the wastewater.