The Effects of Solid Waste Incinerators on Local Communities
Solid waste incineration is a process of burning garbage in order to dispose it. It is a way of reducing the amount of trash that goes into landfills. The solid waste incineration process also allows for the treatment and storage of hazardous and medical wastes.
What is the Use of Solid Waste Incinerators?
Incineration is a process that uses a flame to burn waste. It is an effective way to reduce garbage by up to ninety percent.
Pollution prevention includes reducing energy, water, and hazardous material requirements. It can be achieved through changes in production and raw materials use. Source reduction is the preferred method of decreasing pollutants in a waste stream.
Modern solid waste management plants emphasize source reduction. Waste-to-energy facilities, such as landfills, use incineration to generate heat and electricity.
An incinerator can treat both non-hazardous and hazardous waste. Incinerators are often marketed as a cost-effective alternative to landfills.
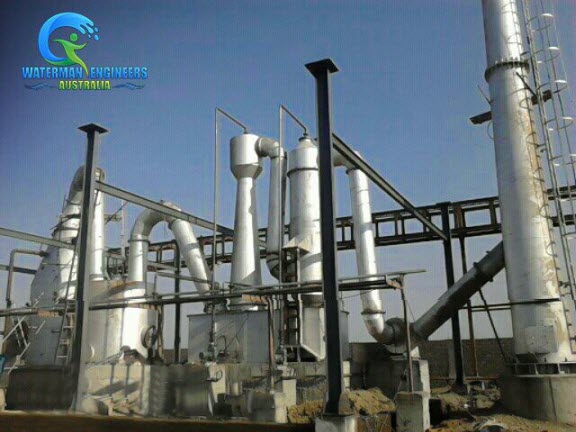
There are dozens of incinerators operating in the US. These facilities handle a small fraction of the nation’s trash. A single incinerator can be used to burn a few hundred tons to several thousand tons of garbage each day.
Most incinerators use low-nitrous oxide burners. Some are equipped with multi-story chimneys for more efficient burning. Larger incinerators are used to treat hazardous waste.
Waste incineration is a popular practice in nations with limited land space. Reliable studies in Europe show that incineration can destroy harmful substances. Fortunately, new technologies are being developed to create construction materials from ash.
The EPA’s goal is to ensure that pollutants are reduced at the source. Its pollution prevention program prevents improper housekeeping and implementing processes that improve process efficiency. To help in this effort, the EPA has established a source-reduction clearinghouse.
Several North eastern states offer economic incentives to attract incineration plants. Cities such as New York are introducing zero-waste policies.
What are the Different Methods for Treatment of Hazardous and Medical Wastes?
Medical waste is a type of waste produced by hospitals, medical facilities, and health care providers. It includes waste from various types of medical activities such as surgery, dentistry, and veterinary care. These wastes may be contaminated by blood and body fluids. Some of them are also highly toxic and can pose a danger to human health.
To control medical and hazardous waste, some states require certification of medical waste treatment technologies. In addition to these regulations, medical waste is also regulated by state and federal environmental agencies.
The first federal act regulating medical waste was the Medical Waste Tracking Act (MWTA) of 1988. The MWTA defined the different types of waste and established a cradle-to-grave tracking system. This was used to record and analyze waste generation. Moreover, it also required labeling, packaging, and management standards.
Since then, the EPA has tightened its standards. This has led to a significant increase in the use of alternative treatments to treat medical waste. However, the number of HMIWIs has decreased.
Another method of treating medical waste is irradiation. For example, an irradiation facility can destroy infectious waste. Using this method, medical waste can be decontaminated.
Another option is autoclaving. Autoclaving is a non-toxic, cost-effective alternative to incineration. The process uses heat in the form of steam to kill microorganisms. While there are no documented health effects associated with autoclaving, it is not recommended for pathological waste.
Incineration is another method of treating medical and hazardous waste. There are several different types of incinerators. Each is designed for a certain purpose. A common incinerator consists of a pit below the incinerator, a hopper for the waste, and a secondary combustion chamber. All these factors work together to provide an effective heat transfer medium.
Treatment of medical and hazardous wastes requires a thorough understanding of the laws and regulations. Consult with your state or local environmental department to learn more about the regulations.
Economic conditions of the Incineration Industry on Local Communities
When considering the economic conditions of the incineration industry, it is important to look at how they are affecting local communities. The effects of incineration facilities on local communities can range from social to economic. However, the exact effects are seldom fully explored.
Incinerators can also produce electricity, and they may provide jobs. However, the number of jobs depends on the type of facility, the characteristics of the population, and the hiring policies. Similarly, a municipality’s capacity for economic growth can depend on the amount of incineration facilities.
Local government agencies can help cultivate favorable attitudes about incineration plants. Such interactions may also foster trust between the two parties. Interactive public consultation mechanisms can assist in reducing the arrogance of the opposition.
Ultimately, understanding how the incineration industry affects local communities is essential to promoting the transition to a more sustainable economy. Understanding local community responses is becoming an important policy focus.
The Bottom Line
A single incinerator can burn several hundred tons of waste per day. Increasing the use of waste-to-energy facilities can help reduce greenhouse gases. Incineration of solid waste has been practiced in the United States for many years.