The Role of Zero Liquid Discharge Systems in China’s Circular Economy Strategy
In China, the circular economy strategy is an essential national priority. It aims to improve resource productivity, reduce energy and water consumption, increase the use of recycled materials, and boost regional resource security.
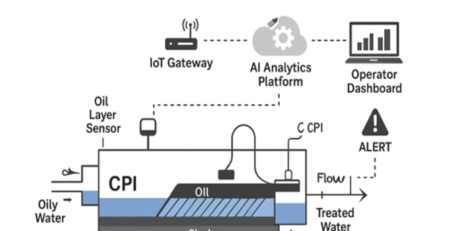
China’s economy has grown rapidly over the past few decades, and along with this growth has come increased industrialization and urbanization. However, this progress has also led to environmental challenges such as water scarcity, water pollution, and climate change. In response to these issues, China has formulated a Circular Economy Strategy to promote sustainable development. A key aspect of this strategy is the implementation of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems. ZLD systems pre-treat industrial wastewater, evaporate it in a brine concentrator and then collect the condensed water for reuse. The waste solids are either sent to a landfill or used as valuable salt by-products.
What is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System?
Zero liquid discharge is a water treatment process that recovers and reuses all of the wastewater that would otherwise be sent to a wastewater disposal facility or evaporation pond. These processes can help industries avoid expensive waste management fees and protect freshwater resources.
ZLD systems use the most advanced wastewater treatment technologies to purify and recycle virtually all of the water that is produced at industrial facilities. These systems also reduce the amount of solid waste that is generated and disposed of at the end of the process.
The basic ZLD system consists of a series of specialized water treatment steps called pre-treatment and concentration. The pre-treatment step is designed to remove simple things from the wastewater stream that can be filtered or precipitated out, conditioning the water and reducing the suspended solids that could foul subsequent treatment steps.
ZLD is a relatively new water treatment approach that focuses on recovering the water and reducing contaminants into solid waste. It is a significant breakthrough in water treatment engineering because it allows industries to reduce costs, improve sustainability, and promote green business goals.
ZLD Systems: A Solution for Water Scarcity in China
Water scarcity is a pressing issue in China, particularly in its northern regions, where water resources are limited. The country’s rapid economic growth and urbanization have placed significant pressure on its water resources, exacerbating the problem. Industrial activities, including manufacturing, mining, and energy production, consume vast amounts of water and generate significant amounts of wastewater, which often contain harmful chemicals and pollutants. ZLD systems offer a solution to this problem by treating industrial wastewater to a high standard and recovering the water for reuse.
ZLD systems also minimize the release of pollutants into waterways. China’s waterways have been severely polluted by industrial activities, with many rivers and lakes being contaminated by toxic chemicals and heavy metals. By treating and recycling wastewater, ZLD systems prevent the discharge of harmful pollutants into the environment, protecting both human health and aquatic ecosystems.
The implementation of ZLD systems has been particularly crucial in areas where water resources are scarce. In recent years, China has faced severe water shortages, particularly in its northern regions. For example, the city of Beijing has relied heavily on groundwater resources, leading to the depletion of aquifers and sinking ground levels. By implementing ZLD systems, industries can reduce their reliance on freshwater resources and ease the pressure on groundwater reserves.
ZLD Systems: A Promising Solution for Sustainable Development in China
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems have emerged as a promising solution for sustainable development in China. As one of the most populous countries in the world, China faces a significant challenge when it comes to managing its limited water resources. At the same time, industrial activities are one of the main sources of water pollution. ZLD systems treat industrial wastewater to a high standard and recover the water for reuse, rather than discharging it into the environment. This approach not only reduces water consumption but also minimizes the release of pollutants into waterways.
ZLD systems align with the principles of the Circular Economy Strategy, which emphasizes the importance of reducing waste, reusing resources, and recycling materials to minimize the environmental impact of economic activities. By implementing ZLD systems, industries can effectively transform industrial waste into valuable resources, contributing to the circular use of resources and the reduction of waste. The treated water can be used for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, cooling, or other industrial processes, reducing the demand for freshwater resources. Furthermore, ZLD systems can also recover valuable materials and resources from wastewater, such as nutrients and metals, reducing the need for new raw materials and minimizing waste generation.
ZLD Systems: A Technological Innovation with Economic Benefits to China
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems are a technological innovation that offers not only environmental benefits but also economic advantages to China. Industries using ZLD systems can recover and reuse water, reducing their water consumption and operational costs. Since water scarcity is a significant problem in China, the ability to reduce water consumption is critical to sustainable industrial growth. By implementing ZLD systems, industries can effectively minimize their reliance on freshwater resources, promoting sustainable management of water resources.
ZLD systems can also generate valuable by-products such as salt, which can be sold or reused. The recovery of valuable by-products reduces the need for raw materials, which can lead to significant cost savings for industries.
ZLD systems are an innovative and cost-effective solution that not only addresses water scarcity and pollution but also offers economic benefits to industries in China. By recovering and reusing water, industries can reduce their operational costs, generate valuable by-products, and enhance their reputation as environmentally.
What are the Challenges of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)?
ZLD systems are a vital component of China’s Circular Economy Strategy, which is based on a “recycle-and-reuse” philosophy. This approach aims to maximize the value of recycled and reused waste materials. It can also help address water scarcity issues.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems are becoming increasingly popular in China due to the country’s growing awareness of the importance of environmental protection and water conservation. However, the implementation of ZLD systems in China also faces several challenges and opportunities, as outlined below:
Challenges:
High capital and operating costs: ZLD systems require significant investment in infrastructure, equipment, and operational costs. The high cost of ZLD systems can be a barrier to their adoption, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises that may not have the financial resources to invest in these systems.
Technical expertise: The operation of ZLD systems requires specialized technical expertise and trained personnel. However, there is a shortage of qualified professionals in China with the necessary skills and knowledge to operate and maintain ZLD systems effectively.
Availability of water resources: The implementation of ZLD systems requires a reliable source of water to achieve their objective of zero liquid discharge. In some areas of China, water resources are scarce, which can make it challenging to implement ZLD systems effectively.
Opportunities:
Research and development: The Chinese people are investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of ZLD systems. The government is also encouraging collaboration between research institutions and industries to develop innovative ZLD technologies.
Water scarcity: China is facing severe water scarcity issues due to its rapid economic growth and industrialization. The implementation of ZLD systems can help to conserve water resources and reduce the burden on existing water infrastructure.
While the implementation of ZLD systems in China faces challenges, such as high costs and a shortage of technical expertise, the Chinese government’s support and investment in research and development provide opportunities for their adoption. With continued efforts to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of ZLD systems, they can play a crucial role in promoting sustainable development and conserving water resources in China.