Induced gas floatation- Treatment of Petrochemical & Refinery Wastewater
Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) Overview:
Induced gas flotation (IGF) cleanses water by eliminating suspended particles such as oils and sediments. suspended matter is removed by induced gas floatation by injecting gas bubbles into the wastewater. This is done in a flotation tank or basin. The suspended matter begins to float as the small bubbles adhere to it, this makes it easy to remove them by a skimming device. This method is most commonly used to treat wastewater effluents from petrochemical plants, oil refineries, chemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries releasing similar wastewater effluents.
In oil industry the induced gas floatation units do not use air as medium for flotation due to risk of explosion. Therefore, instead of air, nitrogen gas is used in induced gas flotation units for such industries to create bubbles.
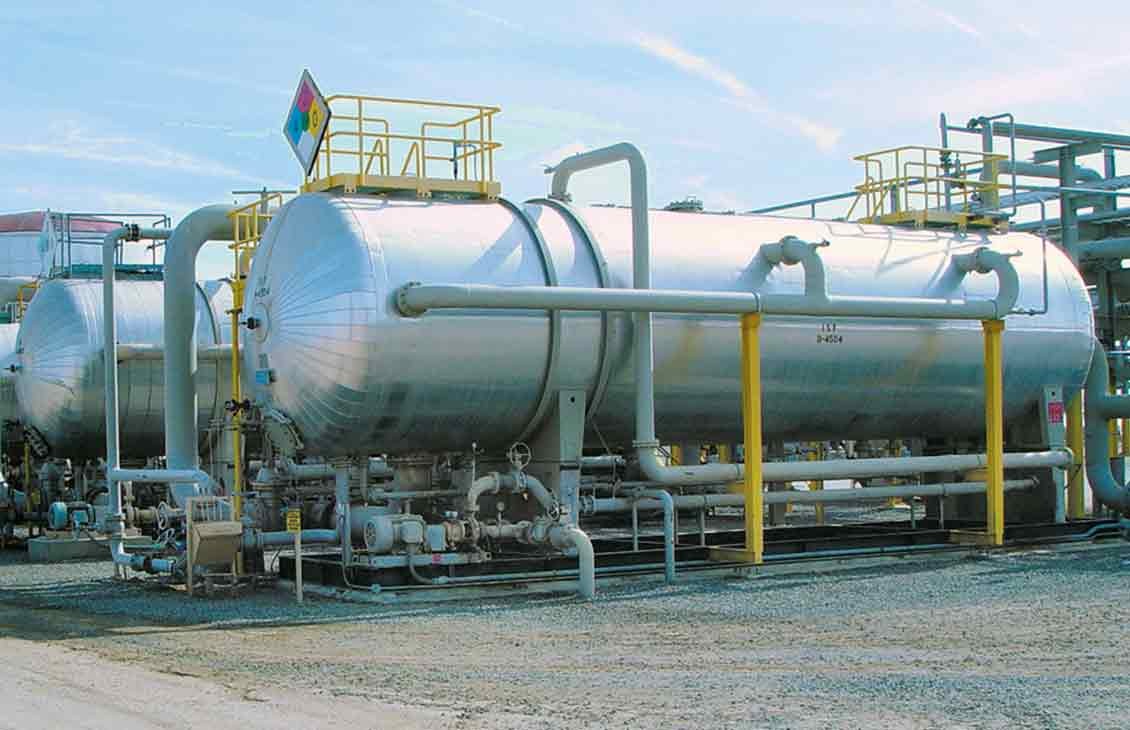

Operating principle:
Induces gas flotation units are hydraulically operated that ensures complete process containment and also efficiently recovers oil from water streams. Induced gas flotation units create gas bubbles that are dispersed through the incoming stream and help in the separation and recovery of oils and fine solid particles present in the water stream. The oil and solid articles float to the surface by adhering to the gas bubbles from where they are removed by skimming device. A side stream of clean water from the induced gas flotation vessel is recirculated and pumped back through an eductor, this process disperses the gas bubbles into to incoming water stream. The small gas bubbles efficiently recover oil droplets present in the water stream due to:
- Bubble/oil attachment high probability.
- Concentrating of bubble is high.
- It has a large surface area/volume ratio of bubbles.
- Rise velocity of bubble is low and have less turbulence.
- With low gas consumption, large volume of gas and solids can be removed.
Induced gad flotation unit has a recirculation system that incorporates a recirculating loop and results in a side stream of water that is taken from the induced gas flotation vessel outlet and then pumped through educator. A gad rich fluid stream of bubbles created by the edcutor is then fed into then induced gas flotation unit and is dispersed through water. Oil removal in induced gas flotation unit can be assisted by acting flocculant or flotation chemicals.
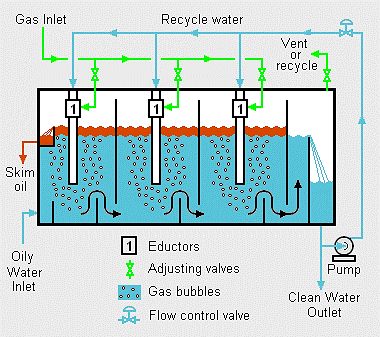
Working:
A hydraulic base technology known as the eductor generators fine bubble dispersion. In some systems, pressure drops taken in the production system by off gassing can produce fine bubble dispersion that is sufficient for flotation. It is important that fine bubble dispersion and produced water are mixed they the fine bubble dispersion is not already formed in the produced water directly. In some units, counter current flow is used in which raw water enters the vessel from the top and at the bottom of the vessel fine bubble dispersion is added. While using this method care should be taken to avoid short circuit of produced water as the fine bubble dispersion can form a less dense column of bulk fluid. This short circuiting of the produced water is called bubble swarming.
Time is required for the bubbles and droplets to engage. Smaller bubbles can be readily engaged with the oil droplets. If the time provided for the engagement is insufficient then even the fineness of bubbles provides limited benefit. Moreover, the efficiency of the unit is also decreased if the shirt circuit is occurring to a significant extent. In some induced gas flotation units, gravitational settling like light centrifugal force can be used to separate the two streams. During the process it is important to remember the tenuous bond that is between the droplet and the bubble. The bubble droplet pairs should be protected by avoiding accelerations and decelerations. Significant water volumes can be carried over the launder by froth skimmers. Significant volume can be added to water carryover from any sloshing occurring due to vessel motion. All bubbles should be considered to be contaminated by oil therefore it is important to minimize the bubble entrainment with the oil lean produced water stream that is exiting flotation unit.
Sub types:
Induced gas flotation process has two sub types:
- Induced gas flotation of the hydraulic kind
- Induced gas flotation of the mechanical type
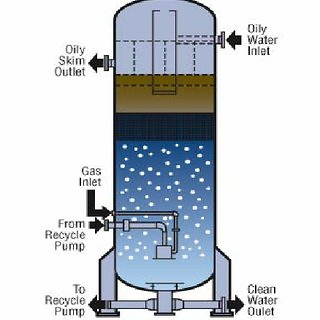
Hydraulic Induced Gas Flotation:
This system consists of a cylindrical vessel that is partitioned into several compartments:
- Floating
- Degassing
- Optional skim storage compartments
- Recirculation pump
- Piping
- Liquid level control system
Hydraulic Induced Gas Flotation Working Principle:
In this system a high velocity stream of recycled clarified water enters the vessel that contain effluent water that enter from the eductor nozzles present at the bottom of the vessel. Recirculation flow of air or gas from the vessel freeboard into the produced water occurs due to this. Small bubbles are uniformly distributed through the cell vessel due to unique arrangement of eductor. The contaminants are lifted by the bubbles to the liquid surface and a froth layer is formed that is then easily skimmed by a simple trough from the liquid surface. Recycling of gas and small volume of recycled water occurs from the degassing chamber into treatment cells.
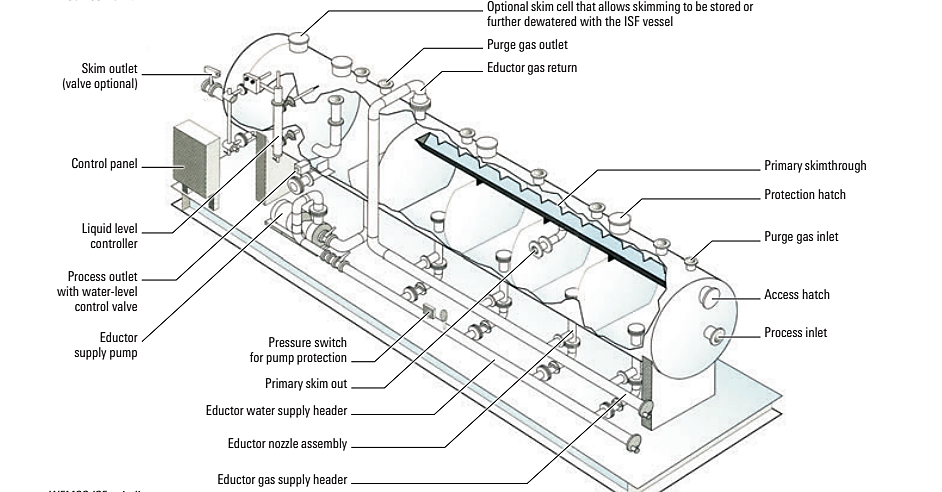
Mechanical Induced Gas Floatation:
In this unit waste water flows horizontally. The unit has four or five chambers or cells. The first four cells are aerated whereas the last one is not. The gas bubbles introduced into the unit carries the oil and solid particles to the liquid layer and forms a froth that can be easily removed by a skimmer. The last cell facilitates the removal of any remaining oil and gas from the water.

Advantages of Hydraulic Induced Gas Flotation:
- It requires either a small amount or no chemical.
- Requires low operation and maintenance manpower.
- Has no internal moving [parts that reduces the time for maintenance.
- Gas high efficiency of oil removal
- Has minimal impact on environment
- There is no fugitive gas emission
Induced Gas Floatation Frequently Asked Questions
1) How does flotation work in wastewater treatment?
Flotation is referred to be a separation process since gas bubbles are used as the transport medium. Because it is hydrophobic or because it has been made to be so, dispersed particulate matter clings to the bubbles and moves against gravity toward the surface of the aqueous solution.
2) How is wastewater treated with Induced gas floatation?
By removing suspended debris like oil or particles, induced gas flotation, or IGF, is a water treatment method that clarifies wastewaters (or other waterways). Gas bubbles are introduced into the water or wastewater in a flotation tank or basin to remove the material.
3) What is the main advantage of using flotation over sedimentation?
The primary benefit of this method is that it generates cleaner material than the sedimentation method. The walls of eggs and cysts frequently collapse during most flotation techniques, making identification difficult.
4) What does DAF stand for in wastewater treatment?
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is a physical/chemical method that has been successfully used to treat a variety of industrial, municipal, and process wastewater streams.
5) What are the advantages of DAF?
DAF contributions are eligible for highly favourable tax treatment as a gift to a public charity. Donors to DAFs are eligible for a federal income tax charitable deduction of up to 60% of their adjusted gross income for cash gifts and up to 30% for gifts of appreciated stock or other assets. Additionally, most DAF assets can grow tax-free.
FAQs about Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) Plants
Que. What is an Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) plant?
An IGF plant is a type of wastewater treatment facility that uses gas bubbles to separate oil, grease, and suspended solids from water.
Que. How does an IGF plant work?
In an IGF plant, gas (usually air) is injected into the water stream, forming bubbles that attach to the contaminants. The buoyant bubbles carry the contaminants to the surface, where they are skimmed off and removed.
Que. What types of industries use IGF plants?
IGF plants are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, food processing, pulp and paper, and wastewater treatment.
Que. What are the advantages of IGF over other treatment methods?
IGF is effective in treating a wide range of contaminants, has a small footprint, and is relatively cost-effective compared to other treatment technologies.
Que. Are there different types of IGF systems?
Yes, there are horizontal IGF systems, vertical IGF systems, and more advanced versions like the dissolved gas flotation (DGF) system.
Que. Can an IGF plant handle high flow rates?
Yes, IGF plants can handle both low and high flow rates, depending on their design and size.
Que. What is the maintenance required for an IGF plant?
Regular maintenance, including cleaning, inspection of equipment, and calibration of instruments, is essential for optimal performance.
Que. Does an IGF plant require skilled operators?
Yes, skilled operators are necessary to monitor and control the IGF system for efficient operation.
Que. Can an IGF plant remove all contaminants from wastewater?
While IGF is effective for various contaminants, it may not remove certain dissolved substances or highly emulsified oils completely.
Que. Are there any environmental concerns with IGF plants?
IGF plants are generally environmentally friendly, as they use air as the gas source and produce no harmful byproducts.
Que. Can an IGF plant treat saline water?
Yes, IGF plants can be designed to handle saline water treatment effectively.
Que. What is the typical lifespan of an IGF plant?
With proper maintenance and upgrades, an IGF plant can have a lifespan of 15-20 years or more.
Que. How energy-efficient are IGF plants?
IGF plants can be energy-efficient, especially when coupled with modern gas injection technologies.
Que. Can an IGF plant handle fluctuating water temperatures?
Yes, IGF plants are designed to handle variations in water temperatures effectively.
Que. What safety measures are required for operating an IGF plant?
Adequate safety measures, including gas detection systems and emergency shutdown protocols, must be in place for safe operation.
Que. What are the space requirements for installing an IGF plant?
The space required depends on the size of the plant and its treatment capacity, but IGF plants are generally compact.
Que. Can an IGF plant be automated?
Yes, many modern IGF plants can be fully or partially automated for increased efficiency.
Que. Do IGF plants require permits for operation?
Yes, obtaining the necessary permits and complying with local regulations is essential before operating an IGF plant.
Que. Can an IGF plant be relocated to a different site?
Yes, it is possible to relocate an IGF plant, but it may require modifications and adjustments to suit the new location.
Que. Are there any byproducts generated during the treatment process?
Depending on the contaminants treated, there might be sludge or other byproducts that require proper disposal or further treatment.
Que. Can an IGF plant be operated in extreme weather conditions?
IGF plants can be designed to withstand a wide range of weather conditions, but extreme conditions may require additional measures.
Que. Can an IGF plant be integrated with other water treatment technologies?
Yes, IGF plants can be integrated with other technologies like chemical treatment or filtration to enhance performance.
Que. Can an IGF plant operate continuously?
IGF plants can be designed for continuous operation or run on batch cycles, depending on the specific requirements.
Que. What are the potential challenges of operating an IGF plant?
Challenges may include handling variable influent qualities, maintaining equipment integrity, and adhering to strict discharge limits.
Que. Does the cost of an IGF plant vary significantly between manufacturers?
Yes, the cost of an IGF plant can vary based on the manufacturer, technology used, and treatment capacity.
Que. Can an IGF plant recover valuable resources from wastewater?
Yes, IGF plants can sometimes recover valuable substances like oil or nutrients from wastewater streams.
Que. Are there any environmental regulations specific to IGF plants?
Environmental regulations for IGF plants may vary by location, so it’s crucial to comply with local laws and standards.
Que. Can an IGF plant be upgraded or expanded as the industry grows?
Yes, IGF plants can be upgraded or expanded to accommodate increased wastewater volumes or stricter regulations.
Que. Are there any water quality parameters that can affect IGF plant performance?
Factors like pH, temperature, and turbidity can influence the effectiveness of an IGF plant and require careful monitoring.
Que. Can an IGF plant be customized for specific industrial processes?
Yes, IGF plants can be tailored to the unique requirements of different industrial processes.
Que. Can an IGF plant help achieve sustainability goals for industries?
Yes, IGF plants can play a vital role in reducing water pollution and promoting sustainable practices.
Que. What is the process of disposing of the separated contaminants from an IGF plant?
The separated contaminants are often collected as sludge and may be treated further or disposed of in compliance with regulations.
Que. How do I determine the appropriate size of an IGF plant for my industry?
Consulting with engineering experts who specialize in IGF technology can help determine the ideal plant size based on your requirements.
Que. Can an IGF plant operate with minimal operator intervention?
While some automation is possible, IGF plants generally require regular operator monitoring and maintenance.
Que. Does the type of gas used in an IGF plant impact its efficiency?
The type of gas used, usually air, can influence the efficiency of the flotation process, but air is commonly used due to its availability and cost-effectiveness.
Que. What are the factors that can cause variations in IGF plant performance?
Variations in influent quality, temperature, gas flow rate, and equipment condition can affect IGF plant performance.
Que. Can an IGF plant handle both organic and inorganic contaminants?
Yes, IGF plants can effectively remove both organic and inorganic contaminants from wastewater.
Que. Is the effluent quality from an IGF plant suitable for discharge into water bodies?
With proper design and operation, the effluent from an IGF plant can meet discharge standards for most water bodies.
Que. Can an IGF plant be used for treating contaminated groundwater?
Yes, IGF plants can be adapted to treat contaminated groundwater in certain scenarios.
Que. Does the quality of the treated water deteriorate over time in an IGF plant?
With regular maintenance and proper operation, the quality of treated water should remain consistent over time.
Que. Can an IGF plant operate with a variable influent flow rate?
IGF plants can handle some variations in influent flow rate, but large and sudden changes may affect their performance.
Que. Can an IGF plant be operated in remote locations with limited access to resources?
Yes, IGF plants can be designed to operate in remote areas with minimal access to resources, but logistical challenges should be considered.
FAQs about Advantages of Waterman Engineers Australia’s IGF Treatment Plant:
Que. What makes Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant stand out from others?
Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant features advanced technology, efficient design, and high-performance capabilities.
Que. What are the key advantages of Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant?
Some advantages include superior contaminant removal efficiency, energy efficiency, compact footprint, and ease of operation.
Que. How does Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant achieve higher contaminant removal efficiency?
The plant incorporates innovative gas injection systems and flotation tank designs that enhance the attachment and removal of contaminants.
Que. Does Waterman Engineers offer customizable IGF plants for specific industry needs?
Yes, Waterman Engineers can tailor IGF plants to meet the unique requirements of different industries and processes.
Que. What kind of industries has Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant successfully served?
Waterman Engineers’ IGF plants have been successfully used in industries such as oil and gas, mining, petrochemicals, and food processing.
Que. Are there any case studies or success stories showcasing the effectiveness of Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant?
Yes, Waterman Engineers can provide case studies and testimonials demonstrating the successful application of their IGF treatment plant.
Que. Does Waterman Engineers offer comprehensive technical support and training for IGF plant operators?
Yes, Waterman Engineers provides technical support, training, and maintenance services to ensure smooth plant operation.
Que. What sets Waterman Engineers’ gas injection system apart from others?
Waterman Engineers’ gas injection system is designed for optimal gas bubble generation, resulting in efficient contaminant separation.
Que. How does Waterman Engineers ensure energy efficiency in their IGF treatment plant?
The plant utilizes energy-efficient equipment and optimized process design to minimize energy consumption.
Que. Can Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant adapt to varying wastewater conditions?
Yes, Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant is designed to handle variations in influent quality and flow rates effectively.
Que. What are the environmental benefits of using Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant?
The plant’s efficient contaminant removal reduces water pollution, contributing to improved environmental sustainability.
Que. Does Waterman Engineers provide post-installation support for their IGF treatment plant?
Yes, Waterman Engineers offers ongoing support, maintenance, and performance monitoring after plant installation.
Que. What is the typical payback period for investing in Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant?
The payback period may vary depending on the industry and scale of the plant, but Waterman Engineers’ plants are known for their cost-effectiveness.
Que. Is Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant compliant with industry standards and regulations?
Yes, Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant is designed to meet relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Que. Can Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant be integrated with existing wastewater treatment systems?
Yes, Waterman Engineers can design their IGF plant to be seamlessly integrated with existing treatment systems.
Que. Does Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant come with remote monitoring capabilities?
Yes, Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant can be equipped with remote monitoring systems for real-time performance assessment.
Que. What measures does Waterman Engineers take to ensure operator safety during plant operation?
Waterman Engineers prioritizes safety in their design and provides safety training to plant operators.
Que. Can Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant be expanded to accommodate future industry growth?
Yes, Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant can be expanded or upgraded to meet increased treatment demands.
Que. What is the typical lead time for acquiring Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant?
The lead time may vary based on project specifics, but Waterman Engineers strives to deliver efficient solutions promptly.
Que. How does Waterman Engineers ensure the long lifespan of their IGF treatment plant?
Waterman Engineers uses high-quality materials, robust construction, and regular maintenance practices to ensure the plant’s longevity.
Que. Are there any success stories of cost savings achieved through Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant?
Yes, some industries have reported significant cost savings on wastewater treatment expenses after implementing Waterman Engineers’ plant.
Que. Does Waterman Engineers provide pilot testing services for their IGF treatment plant?
Yes, Waterman Engineers may offer pilot testing services to validate the plant’s performance for specific applications.
Que. What environmental awards or certifications has Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant received?
Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant may have received recognition or certifications for its eco-friendly and sustainable features.
Que. Can Waterman Engineers provide references from clients who have installed their IGF treatment plant?
Yes, Waterman Engineers can provide references or connect prospective clients with their satisfied customers.
Que. Does Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant offer operational cost savings over the long term?
Yes, the energy-efficient design and superior contaminant removal capabilities can lead to long-term cost savings.
Que. How does Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant compare to other wastewater treatment technologies in terms of performance?
Waterman Engineers’ IGF plant is known for its high removal efficiency and competitive performance compared to other technologies.
Que. What is the warranty coverage for Waterman Engineers’ IGF treatment plant?
The warranty coverage period may vary, and it’s best to inquire with Waterman Engineers directly for specific details.









