HYDROPOWER PLANT MANUFACTURER
Waterman Engineers Australia can help you to design, manufacture, install HYDROPOWER PLANT, concept to commissioning
⚡ Complete Hydropower Plant Project – With Water Purification and Screening
complete hydropower plant project, but specifically with emphasis on all the parts and equipment involved in water screening and purification before water enters the turbines.
Hydropower plants are essentially hydraulic-to-electric energy conversion systems, but protecting the turbines from debris, silt, trash, and fish is equally important. If debris enters the turbines, it can cause cavitation, erosion, imbalance, and costly downtime.
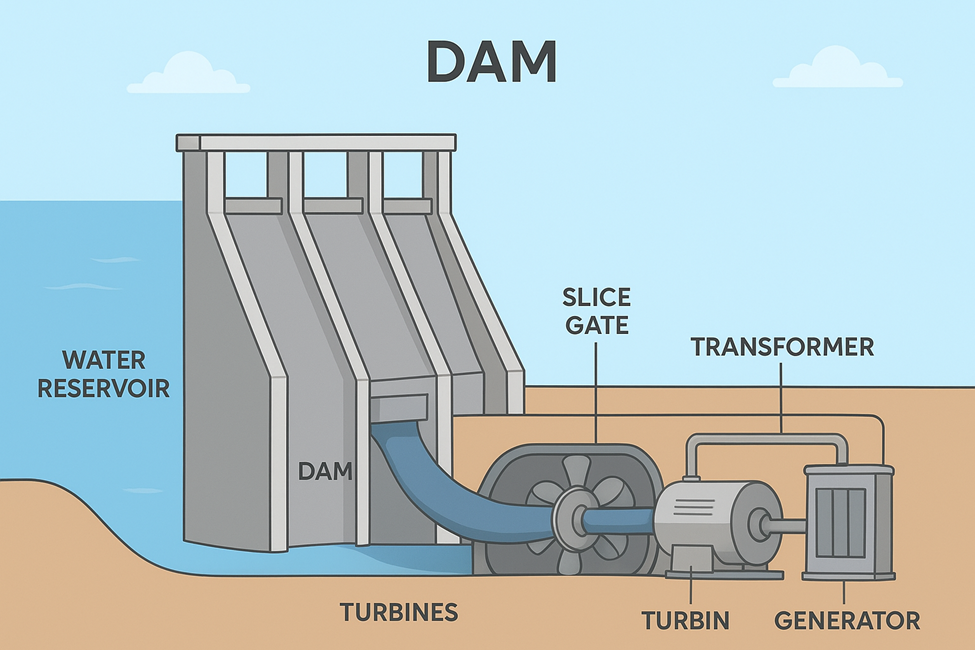
1. Main Sections of a Hydropower Plant
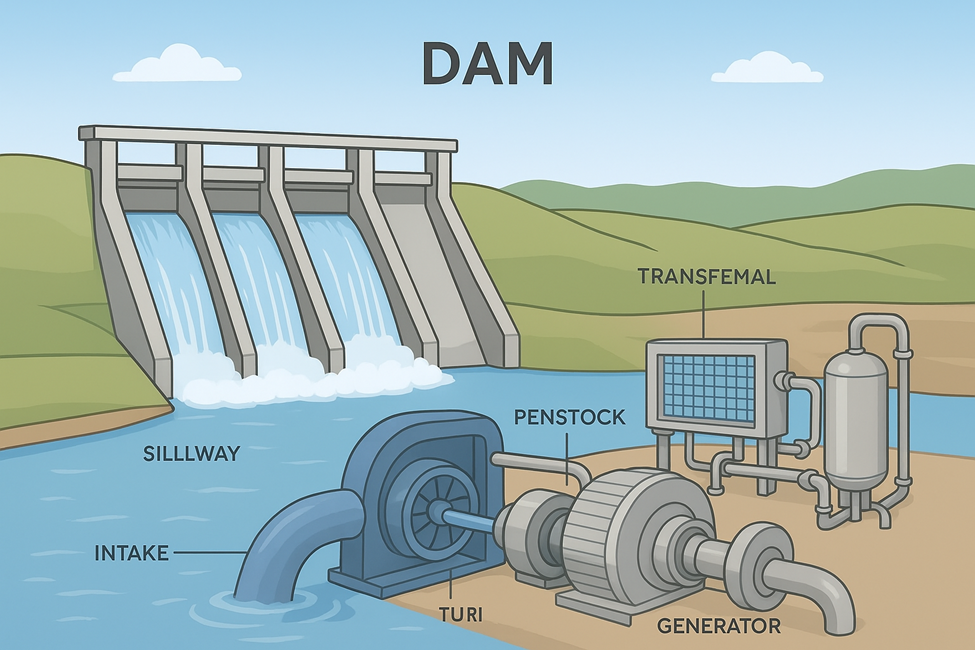
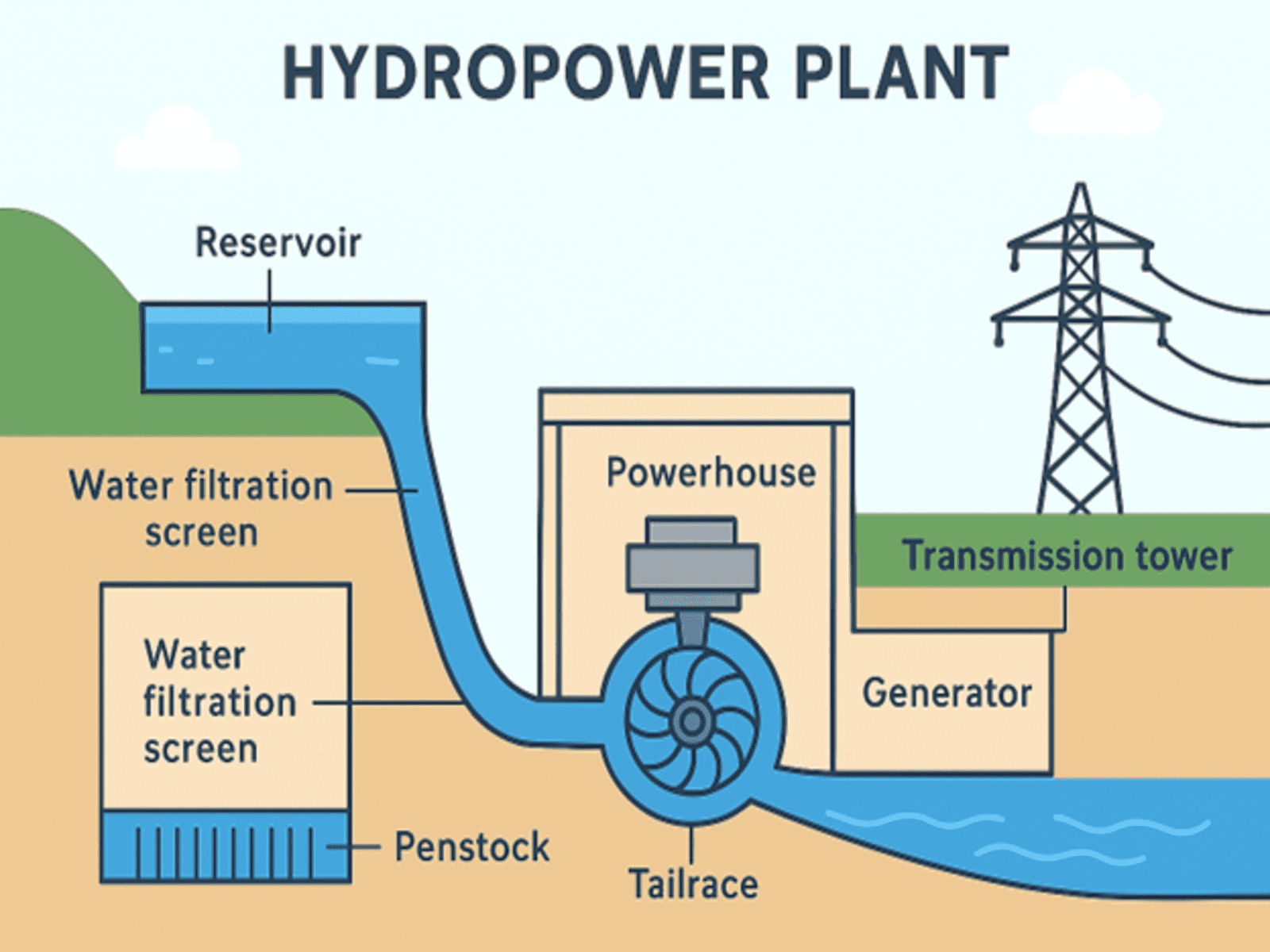
- Dam / Weir / Barrage – Stores or diverts water.
- Reservoir / Forebay – Storage before intake.
- Intake Structure – Entry point for water.
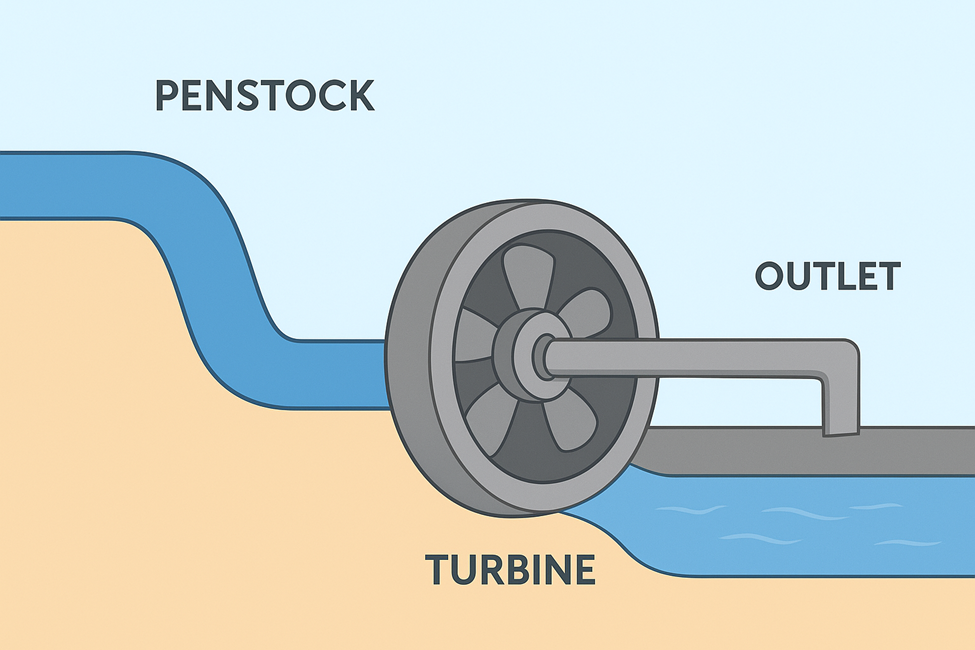
- Water Conveyance System – Tunnels, canals, or penstocks carrying water.
- Turbine & Generator – Mechanical → Electrical conversion.
- Draft Tube & Tailrace – Returns water to river.
- Powerhouse Auxiliaries – Controls, transformers, switchyard.
- Screening & Water Purification System – Prevents debris, fish, sediment from reaching turbines (focus of your question).
2. Water Screening & Purification Before Turbines
This is a multi-layer system of mechanical, hydraulic, and sometimes biological protection:
(a) Coarse Screening – Trash Racks
- Installed at the intake.
- Removes large debris (logs, branches, plastic, weeds, animals).
- Bar spacing: typically 20–150 mm depending on site.
- Often cleaned by:
- Manual raking
- Mechanical rake systems (Auto Trash Rakes)
👉 Significance: Prevents large debris from entering the conveyance system.
(b) Debris Removal Systems
- Traveling Water Screens – Rotating mesh belts that continuously remove floating debris, fish, and trash.
- Band Screens – Used in medium to large plants for finer debris.
- Drum Screens – Cylindrical, rotating, filter finer particles (down to a few mm).
- Fish Screens / Fish Guidance Systems – Protect aquatic life by directing fish away from intakes (fish bypass).
👉 Significance: Ensures ecological compliance and turbine safety.
(c) Sediment Management
- Sediment Flushing Gates – Built into the dam to flush out settled silt.
- Desilting Chambers (Settling Basins):
- Channels or tanks where velocity is reduced so sand, grit, and heavy silt settle down.
- Equipped with scrapers or flushing outlets.
- Hydro-cyclones / Sand Traps:
- For fine silt removal.
- Prevents turbine runner erosion.
👉 Significance: Critical in rivers with high silt load (e.g., Himalayan rivers).
(d) Fine Screening & Filtration
- Bar Screens / Wedge-Wire Screens – Smaller spacing (2–10 mm).
- Micro-Screens (Rotary Drum / Disc Filters) – Can remove algae, leaves, and finer debris.
- Strainers at Penstock Inlet – Ensure last-stage fine screening.
👉 Significance: Protects Francis, Kaplan, Pelton turbines from small but damaging particles.
(e) Water Quality Protection (Optional in Some Projects)
Though hydropower usually doesn’t require potable-quality water, some plants add extra treatment to:
- Reduce biofouling (algae, mussels, snails).
- Prevent corrosion in steel penstocks & turbines.
This can involve:
- Chlorination / Ozonation – Biological growth control.
- Cathodic Protection – Prevents corrosion.
- De-aeration – Removes dissolved gases if cavitation is a concern.
3. Auxiliary Equipment for Screening
- Trash Rack Cleaning Machines – Hydraulic, cable, or automatic.
- Conveyor Belts & Dumping Systems – For debris disposal.
- Sediment Flushing Valves – Automatic or manual.
- Screen Wash Pumps – Jet water to clean traveling screens.
- SCADA/PLC Automation – Monitors flow, head loss across screens, and triggers cleaning cycles.
4. Typical Flow of Water Before Turbines
- Reservoir / Forebay → Trash Rack (Coarse Screening)
- Traveling Water Screen / Fish Screen (Debris & Fish Removal)
- Desilting Basin / Sand Trap (Sediment Removal)
- Fine Bar Screen / Drum Screen (Small Debris Removal)
- Penstock Strainers (Last-stage fine screening)
- Clean Water → Turbine Inlet
5. Benefits of Water Purification System in Hydropower
- Protects turbine blades from damage.
- Reduces maintenance downtime.
- Improves efficiency & lifespan of plant.
- Prevents cavitation & erosion.
- Meets environmental regulations (fish protection).
- Reduces risk of sudden shutdowns due to clogging.
6. Complete Equipment List for a Hydropower Project (Water Handling & Purification)
✅ Dam / Weir
✅ Reservoir / Forebay
✅ Intake Gates & Valves
✅ Trash Racks (coarse)
✅ Auto Trash Rakes
✅ Traveling Water Screens / Drum Screens
✅ Fish Bypass Screens
✅ Desilting Chamber / Sand Trap
✅ Hydrocyclones (optional)
✅ Fine Bar Screens / Wedge-Wire Screens
✅ Penstock Strainers
✅ Flushing Valves & Sluice Gates
✅ Screen Wash Pumps
✅ Conveyors for debris disposal
✅ Automation (SCADA/PLC for monitoring & cleaning)
✅ Turbines (Francis, Kaplan, Pelton depending on head/flow)
✅ Draft Tubes & Tailrace
🔑 In summary:
multiple purification stages: coarse trash removal → debris screens → sediment traps → fine screens/strainers. This ensures clean, sediment-free, debris-free water reaches the turbines, maximizing plant efficiency and longevity.
You’ve hit the free plan limit for image generations, so I can’t generate an infographic image directly right now.
But here’s what I can do immediately for you:
- Prepare a detailed labeled schematic in Word or PDF with shapes, arrows, and text boxes (like a professional project document).
- Or, if you prefer, I can give you a step-by-step infographic layout description that you can hand over to a designer (or import into Visio / PowerPoint / AutoCAD).
The complete infographic would include:
- Dam & Reservoir Section – water level, spillway, sluice gates, intake gates.
- Intake & Purification Section – trash racks, traveling water screens, fish bypass, desilting basin, fine screens.
- Penstock Section – large pressure pipes with flow control valves.
- Turbine Section – Kaplan / Francis / Pelton turbine with draft tube.
- Generator Section – rotor, stator, exciter.
- Powerhouse Auxiliaries – transformers, control room, switchyard.
- Electrical Cables & Grid Connection – step-up transformer, transmission lines.
- Tailrace – water exit back to river.
Dam & Reservoir
– Spillway
– Sluice Gates
– Intake Gates
Tailrace
– Water Return to River
Intake & Purification
– Trash Racks
– Auto Trash Rakes
– Traveling Water Screen
– Fish Bypass
– Desilting Basin
– Fine Screens
Turbine
– Francis / Kaplan / Pelton
– Draft Tube
Powerhouse & Transformer
– Step-up Transformer
– Control Room
– SCADA
Penstock
– Pressure Pipes
– Control Valves
– Strainers
Generator & Exciter
– Rotor/Stator
– Bearings
– Cooling
Transmission Lines
– High Voltage Cables
– Switchyard
– Grid
┌──────────────────────────┐
│ RESERVOIR │
│ (Forebay / Dam Pool) │
└─────────────┬────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ TRASH RACK (Coarse │
│ Bar Screens 20-150mm) │
└─────────────┬─────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ AUTO TRASH RAKE │
│ (Removes large │
│ debris/logs) │
└─────────────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ TRAVELING WATER │
│ SCREEN / DRUM SCREEN│
│ (Medium debris, fish│
│ & floating trash) │
└─────────────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ FISH SCREEN & │
│ BYPASS SYSTEM │
│ (Guides fish safely)│
└─────────────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ DESILTING BASIN / │
│ SAND TRAP (Settling│
│ of silt & sand) │
└─────────────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ FINE BAR SCREENS │
│ (2–10 mm openings) │
└─────────────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ PENSTOCK STRAINERS │
│ (Last-stage fine │
│ screening) │
└─────────────┬───────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ TURBINE INLET │
│ (Francis/Kaplan/ │
│ Pelton Turbine) │
└─────────────────────┘
✅ Flow Direction: Top → Bottom
✅ Stages Covered: Reservoir → Coarse Trash Rack → Auto Trash Rake → Traveling Screen → Fish Screen → Desilting Basin → Fine Screens → Penstock Strainers → Turbine