Water Screens Manufacturer in Hydroelectric Power Stations
Various screens used to filter water before entering turbines in hydroelectric power stations. Each type serves as a barrier at different stages of intake, protecting the plant from debris, silt, and biological matter.
🔹 Water Screens Manufacturer in Hydroelectric Power Stations
1. Coarse Screens (Trash Racks)
- Function: First line of defense at the reservoir or river intake.
- Construction: Heavy-duty steel bars with spacing typically 50–150 mm.
- Purpose: Stops large debris like logs, branches, plastics, ice blocks, and stones.
- Features:
- Simple, robust, fixed structure.
- Often cleaned using auto trash rakes.
- Must withstand high hydraulic pressure & impact loads.
2. Medium Screens (Bar Racks / Fine Trash Racks)
- Function: Provide intermediate filtration after trash racks.
- Construction: Steel or stainless-steel bars with 10–50 mm spacing.
- Purpose: Removes medium-sized debris, aquatic plants, and floating waste that pass coarse racks.
- Use: Often installed in front of traveling water screens for pre-screening.
3. Fine Screens (Traveling Water Screens)
- Function: Continuous removal of fine debris.
- Construction: Moving panels or mesh screens (openings 3–20 mm).
- Working: Panels rotate in a loop; debris is lifted and washed off by spray jets into a trough.
- Purpose: Filters small wood pieces, weeds, fish, plastics, algae mats.
- Features:
- Self-cleaning, automated.
- Protects turbines and cooling water systems.
- Can be designed with fish bypass systems for environmental compliance.
4. Drum Screens / Rotary Screens
- Function: Provide very fine screening at critical water intakes.
- Construction: Cylindrical drum with wire mesh or perforated panels (openings as fine as 2–5 mm).
- Purpose: Removes small debris, silt, algae, fish larvae.
- Features:
- Rotates slowly; water flows through drum surface.
- Debris removed by spray water jets or brushes.
- Commonly used in cooling water channels for hydro & thermal power plants.
5. Micro Screens / Wedge Wire Screens
- Function: Used where high water clarity is required.
- Construction: Stainless steel wedge wire mesh; openings down to 1–2 mm.
- Purpose: Filters fine sediments, suspended solids, plankton.
- Features:
- Low head loss due to wedge design.
- Sometimes used as secondary filtration for turbine cooling systems rather than main penstock.
6. Fish Protection Screens
- Function: Specialized screens to protect aquatic life.
- Types:
- Inclined Bar Screens → Fish slide along to bypass channel.
- Rotary Fish Screens → Drum or disc type, guiding fish safely back to river.
- Purpose: Ensure environmental compliance, prevent turbine fish kills.
- Mesh size: Typically 3–10 mm, depending on fish species.
7. Automatic Self-Cleaning Screens
- Function: Smart filtration systems for modern unmanned hydro stations.
- Working: Use backwash jets, suction nozzles, or brushes to clean mesh automatically.
- Purpose: Reduce manual maintenance, maintain consistent hydraulic performance.
- Features: Integrated with SCADA/IoT for remote monitoring of head loss and debris load.
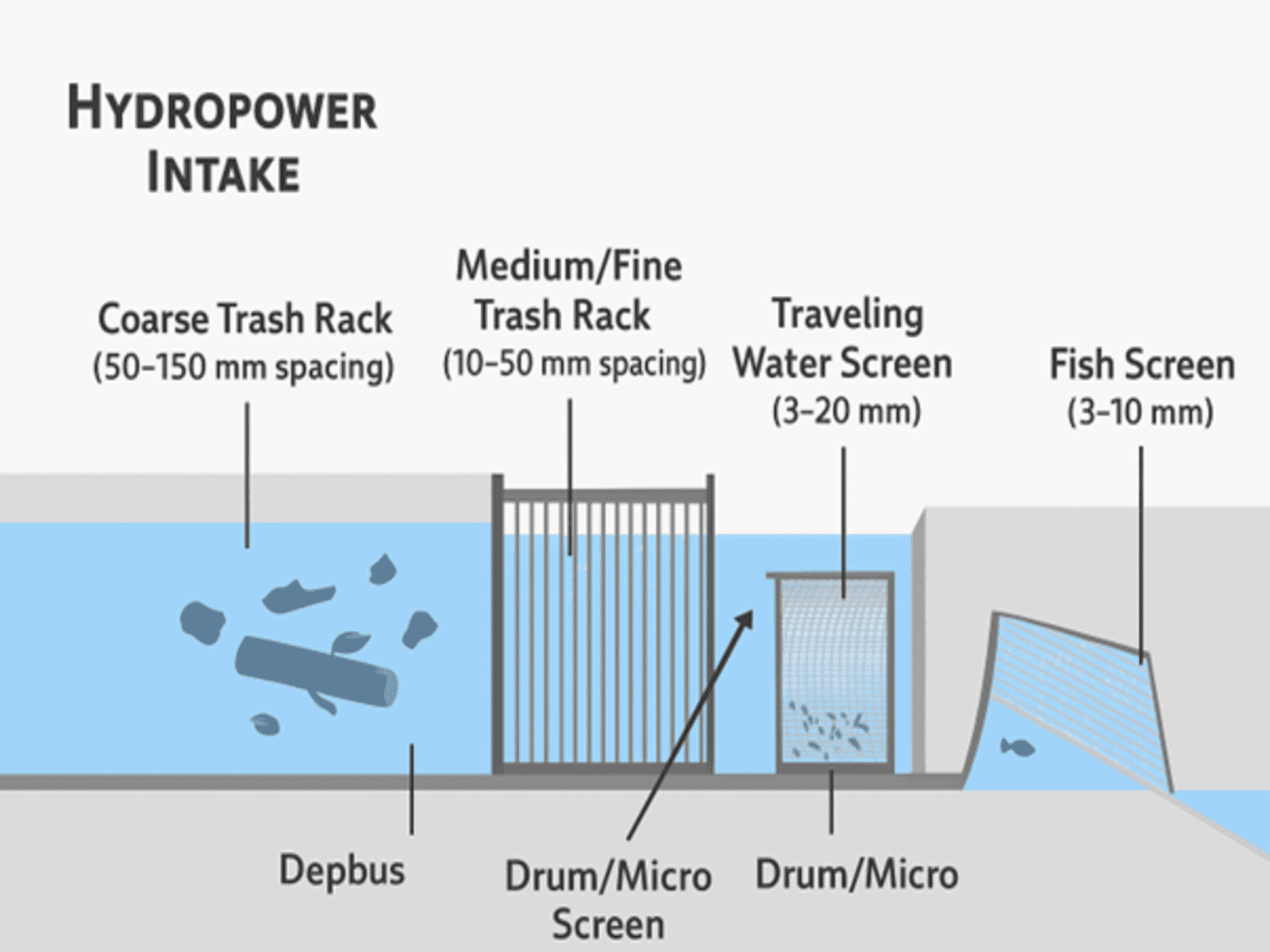
🔹 Typical Water Screening Arrangement at Hydropower Intake
- Coarse Trash Rack (50–150 mm spacing) → Blocks logs, stones, large debris.
- Medium/Fine Trash Rack (10–50 mm spacing) → Stops medium debris.
- Traveling Water Screen (3–20 mm) → Continuous cleaning, protects turbines & cooling.
- Drum / Micro Screens (0.1–5 mm) → Optional, for fine protection & cooling water systems.
- Fish Screens (3–10 mm) → Installed where biodiversity protection is mandatory.
✅ In summary:
Hydroelectric power stations use a multi-stage screening system — starting with coarse trash racks, moving through traveling fine screens, and optionally ending with drum/micro screens for cooling water — all working together to protect turbines, optimize efficiency, and safeguard the environment.