Water Filtration Plants
What is a Water Filtration Plant? In simple terms, it is a filtration system that uses a filter and a medium to remove suspended particles from a fluid. It is used for drinking water, wastewater, industrial manufacturing, and food and beverage production facilities. Water filtration can remove suspended particles and decrease the amount of bacteria, viruses, and parasites found in water. It can also remove chemicals that can cause health problems, including chloramines, nitrates, and other chemicals.
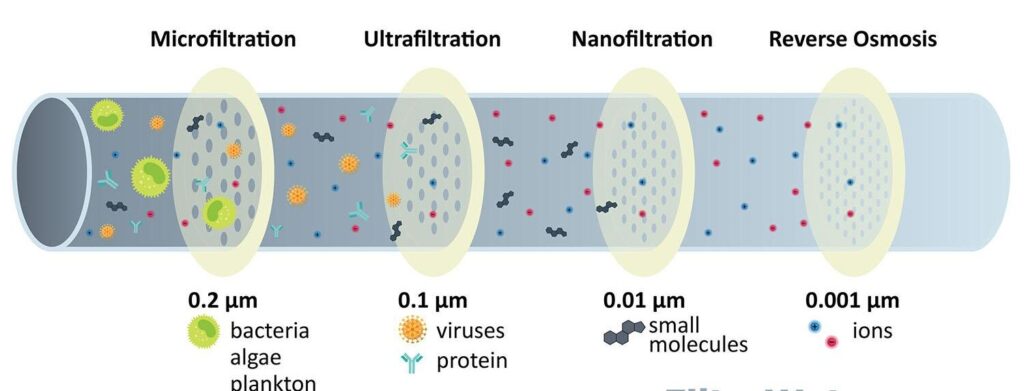
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis water re-filters dissolved solids and suspended solids from water. The process works by forcing water through a semi permeable membrane, similar to the one inside a plant cell. The water passes through the membrane, while larger molecules are blocked. The water flows back and forth until the concentrations of all the constituents are equal. The filtered water is then discharged to a waste stream.
Reverse osmosis water filtered by reverse osmosis systems are considered to be the most effective way to purify water. These systems filter water using the natural process of osmosis to remove a significant portion of contaminants. The water that is cleaned by these systems is referred to as permeate and the concentrated water is called waste. These systems are available in a variety of configurations, ranging from a single faucet to a whole house system.
Gravity Filtration
Among the different types of water filtration processes, gravity filtration is one of the oldest and most common. This method uses concrete tanks with a grating at the bottom to collect the water. The water is then filtered as it flows through the layers of graded sand. The filtered water is returned to the drinking supply via perforated pipes. The filters may be open or closed. For more information, visit the official Wikipedia article on gravity filtration.
The upper chamber of a gravity water filter contains the filter element. This element has microscopic pores that enable the water to pass through it and be filtered. Once the filtration process is complete, the purified water is collected in a tank beneath the filtration system. Unlike other methods, gravity filtration does not require electricity or plumbing to work. Instead, water flows over the filters due to the weight of the filter element.
The parts of a gravity filtration system are separated by granular filter media. The granular filter media have effective sizes ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 mm. Most applications use this technique to remove color and solids larger than ten or twenty microns. Coagulating chemicals are used to remove the smallest particles. The conditioned raw water is introduced at the top of the basin and flows downward through the media bed to be collected by an under-drain system. A sludge-removal process is required periodically.
Land and Peat Moss Filters
Peat and land moss are both excellent natural water filters. The peat bed is suitable for landscape applications and can reduce suspended solids, BOD5, FC, and turbidity by as much as 96%. The peat bed reduces odour, nuisance, and insects, and can be used at lower dosing rates than peat moss. These water filters are also available at a wide variety of prices.
Peat is rich in nutrients, and it can maintain a high temperature. The peat also contains nutrients, vitamins, and carbohydrates that can promote relaxation and a stimulating blood stream. Furthermore, peat contains humic acid, lipids, and trace minerals. Peat is also a good source of fuel in some countries, and it is used in Ireland, Russia, and Finland for heating.
Before the introduction of bio filtered water, polluted water first passed through the sand and the peat moss. These substances acted as grit chambers for the water and filtered the solids. Peat moss, on the other hand, softens water by binding calcium and magnesium ions, releasing Gallic and tannic acids, and reducing pH and carbonate hardness.
The uranyl ion in peat is highly soluble and forms a range of complexes with the sorbent. The resulting compounds are highly mobile in the peat-water system. They are highly mobile in the water, and they are present in many commonly used products, such as fertilizers and gypsum. Moreover, peat moss filters reduce the pH of dissolved organic matter and improve water filtration.
Ozone Water Filtration
Ozone water filtration plants have several advantages over other filtration processes. They can quickly remove most organic matter, but the oxidized matter must be removed by bio-filtration. Ozone also kills micro-pollutants in surface water, but these need to be removed during the next water purification process. In addition, drinking-water standards for pesticides in the European Union are strict, requiring 0,1 mg of each compound per litre of water.
Ozone generators are highly sophisticated and require a high amount of electricity. However, these devices are relatively cheap to operate. Depending on the model, you may need to perform periodic maintenance on the generator, UV lamp, and pumps. Some ozone systems include pre-treatment and post-treatment devices, which require additional maintenance. Ozone leak detection is a major safety feature of the unit, and some of these devices sound an alarm or activate a warning light if they detect a problem.
In addition, ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent with a high redox potential. Because it is a powerful oxidizing agent, ozone does not produce by-products, and it effectively treats micro-pollutants that are untreated by the traditional activated sludge process. Ozone systems are also easy to install, which makes them a great option for retrofitting existing water systems.
Distillation in Water Filtration Plant
The process of water distillation has been around for centuries. This method of removing contaminants from water dates back to at least 200 AD. It is simple and based on the natural cycle of water, and there are few components needed to make it work. Distillation is an effective method for removing contaminants in water, especially when paired with a reverse osmosis water filter. Distillation in water filtration plants is not for everyone.
A distillation process removes most dissolved materials. It also kills biological contaminants. However, some volatile organic compounds may not be completely removed. For instance, some organic compounds will vaporize when heated, but will remain in the purified product. Distillation methods can use solar or multistage flash distillation. In both cases, distillation can reduce the levels of organic contaminants. In general, a water distillation system can reduce biological contaminants, sediment, and metals.
Distillation can also remove a wide range of contaminants, including lead, asbestos, and chromium. Typically, distillation is used in large-scale water filtration plants. Stainless steel is the material used for distillation, and it uses a high-powered fan to speed up the cooling process and convert vapor to liquid. These methods are both effective and cost-effective. The water purification process is an essential part of water filtration, and distillers are an excellent choice for those who wish to improve their drinking water quality.
Disinfection
The efficacy of disinfection depends on the amount of chemical agent used and its composition. Its dosage should not pose a health risk to end users, but should have minimal negative effects on the aesthetic quality of finished water. The dosage of a disinfectant must also be calculated taking into account the amount of residual that remains after the disinfection process. In addition, the volume of water that has to be stored for distribution to a distribution system may be huge, requiring large areas of land.
In addition, water treatment plants use chemical disinfectants to kill any remaining bacteria, viruses, and parasites. This disinfectant is then filtered out of the water and returned to the community. However, if the remaining bacteria, viruses, and parasites survive the disinfection process, the resulting water is not safe for drinking. As a result, water treatment plants ensure that the level of chemical disinfectant is very low when the water leaves the treatment plant.
In addition to chlorine disinfection, the other treatment steps, such as chlorination, also play a role in the bacterial community composition. These bacteria may help the filtration process by biodegrading contaminants. However, some bacteria may be human pathogens, and therefore pose a health risk to consumers.